
There are about 16 million people in the United States alone who have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This condition is characterized by slow but persistent lung function decline that leads to breathlessness, chest pain, and fatigue. Several lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the rate at which COPD progresses including an improved exercise routine, a refined diet, inhaled medications, and most importantly, oxygen therapy. Every case of COPD is different, however, so patients should consult with their doctor to learn which lifestyle changes will benefit them.
{{cta('fa8abc2a-1e88-4fa3-82fd-1cb5b9ed43b2','justifycenter')}}
When it comes to supplemental oxygen therapy, there tends to be a lot of confusion over the different devices that are available to COPD patients. Many people are told that they need medical oxygen, but they’re never provided with instruction on finding an oxygen device that meets their needs. In this post, we’ll discuss three different types of medical oxygen: compressed oxygen, liquid oxygen, and oxygen concentrators. You’ll learn the differences between them and you’ll receive some guidance for choosing one that fits your lifestyle.
If you still have questions after reading, be sure to reach out to our oxygen device specialists here at LPT Medical. We’ll walk you step-by-step through choosing an oxygen device, getting the best deal, and even helping you to receive the necessary medical paperwork. Give us a call at 1-888-416-3855 or email us at info@lptmedical.com.
What is Compressed Oxygen Gas?
Compressed oxygen gas refers to oxygen that has been stored within a tank or a cylinder. Oxygen has been stored in this way since 1868 and it’s still considered a viable method to this day; albeit, the technology has certainly evolved. Compressed oxygen gas is used for a variety of purposes, but it’s primarily used for industrial and medical settings. Many COPD patients use oxygen tanks on a daily basis to maintain the oxygen levels in their blood. For the most part, oxygen tanks are reliable for oxygen therapy, but there are some downsides that you should be aware of.

One of the most notable downsides of oxygen tanks is that they are heavy and bulky. Chances are, you’ve seen people carrying an oxygen tank around in public, and it’s not hard to see how much they struggle. Portable oxygen tanks can weigh as much as 20 pounds and they have a very oblong shape that makes them difficult to carry at your side or on your back. Most people choose to put their oxygen tank on a rolling cart but this comes with problems of its own. They take up a lot of space and they’re difficult to maneuver around obstacles or up a flight of stairs. Home oxygen tanks can weigh well over 100 pounds meaning you will need professional help just to move one.
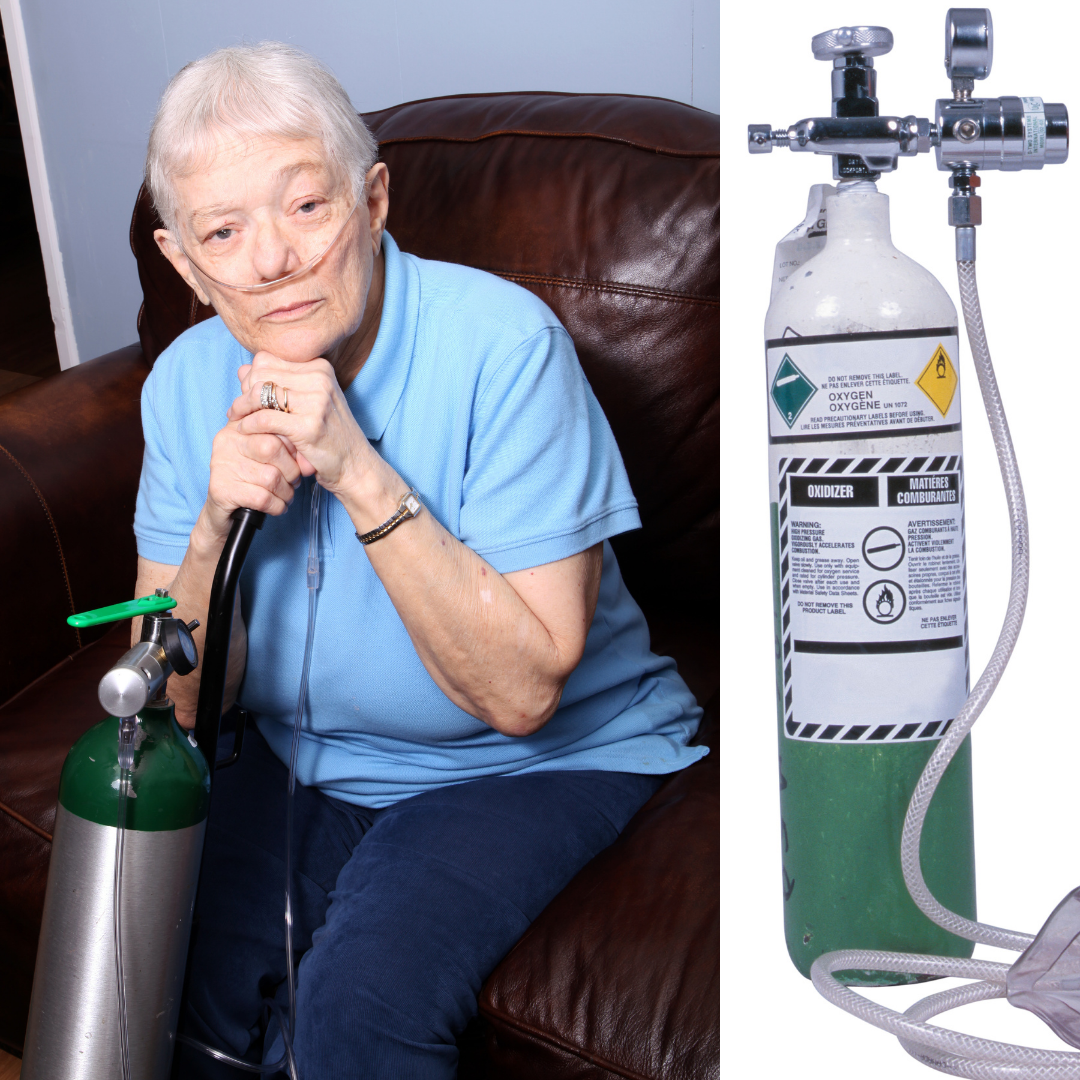

Another glaring problem with oxygen tanks is that they need to be refilled constantly. For example, an “E” tank that is about 3 feet tall and weighs 8 pounds will only last 5 hours if it’s used continuously. At this point, you are going to either have to run home and use your home fill station or find a dependable oxygen company that can refill or replace your oxygen tank for you. All of this takes time and money, all while distracting you from what you care about most. It’s important to remember that the only way to extend the duration of your oxygen supply is to carry a bigger and bulkier oxygen tank or purchase a device called an oxygen conserver.
What is Liquid Oxygen?
Liquid oxygen is similar to compressed oxygen in that the oxygen is stored in a tank. The difference is that these devices store the oxygen in its liquid state rather than as a gas. This is preferable over compressed oxygen because once oxygen enters its gaseous state it expands and thus takes up more space. Liquid oxygen canisters tend to be much smaller and lighter than compressed oxygen and they last longer without needing to be refilled. There are some downsides to these units, however, so let’s take a look.

Likely the first thing you’ll notice about liquid oxygen devices is that they are more expensive than traditional oxygen tanks. This is because — in order for oxygen to be stored in a liquid state — it needs to be kept at very low temperatures. And in order to do that, you need a special type of storage container. Liquid oxygen cylinders work like a thermos in that they keep the liquid oxygen at around -297 degrees Fahrenheit. For safety reasons, liquid oxygen cylinders have decompression vents that release oxygen as the unit warms up. This means you should use it right after filling it up to ensure no oxygen is lost.

One of the problems many people encounter with liquid oxygen is that it’s extremely difficult and expensive to refill. You’ll need to either have a special home fill reservoir or you’ll need to outsource to an oxygen company. Even then, you may be hard-pressed to find a company that is able to fill a liquid oxygen device. While liquid oxygen tanks provide many benefits over traditional oxygen tanks, they aren’t as popular simply due to the high barrier of entry.
What is an Oxygen Concentrator?
The third and final oxygen device we’ll discuss is oxygen concentrators. Unlike traditional and liquid oxygen tanks which hold oxygen inside the unit, oxygen concentrators draw in ambient air, remove gases like nitrogen and argon, and output medical-grade oxygen. Another thing that sets concentrators apart is that they are electronic devices. What this means is that they need a reliable source of energy in order to operate. There are three different types of oxygen concentrators so we’ll break each one down.
Stationary Oxygen Concentrators
Also called home oxygen concentrators, stationary oxygen concentrators need a constant source of power in order to operate. The unfortunate downside to this is that you won’t be able to leave the house without there being an interruption in your oxygen delivery. On the other hand, you can still use things like extension cords or extra long nasal cannulas in order to move around the room freely. Despite the name “stationary,” most of these oxygen devices have wheels on the bottom that make them easier to move around the house. However, they tend to weigh a lot (usually upwards of 30 pounds).
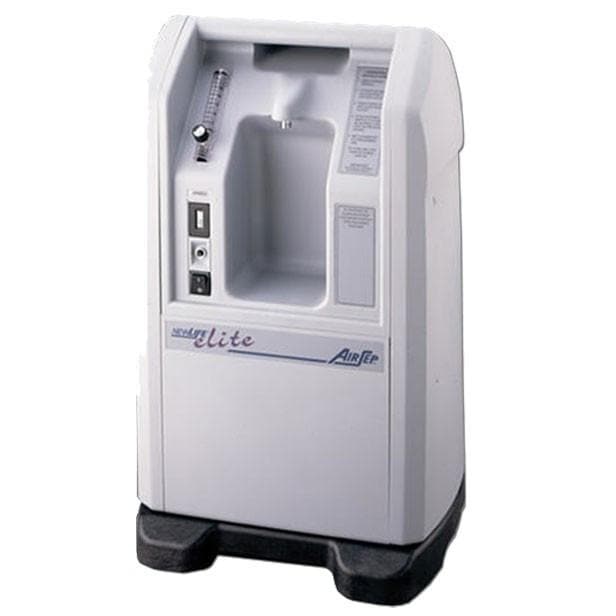

One of the main reasons stationary oxygen concentrators are still in use today is because of their high oxygen output. Some concentrators like the NewLife Intensity 10 can put out up to 10 LPM (liters per minute) of oxygen which is enough for people with severe COPD. They’re also extremely reliable and they can run 24 hours a day and 7 days a week without a problem. Stationary concentrators are not ideal for people who want to get out and about but they’re a good choice for people who stay around the house.
Continuous Flow Portable Oxygen Concentrators
A portable oxygen concentrator works the same way as a stationary oxygen concentrator, but instead of being plugged into a wall outlet 24/7, POCs run off of rechargeable batteries. Most POCs use lithium-ion batteries which are some of the most powerful and reliable batteries in use today. You can find them inside cellphones, laptops, and other electronic devices. The term “continuous flow” refers to the way that oxygen is administered to the patient. It simply means that the oxygen is being released in a constant stream regardless of your breathing rate.
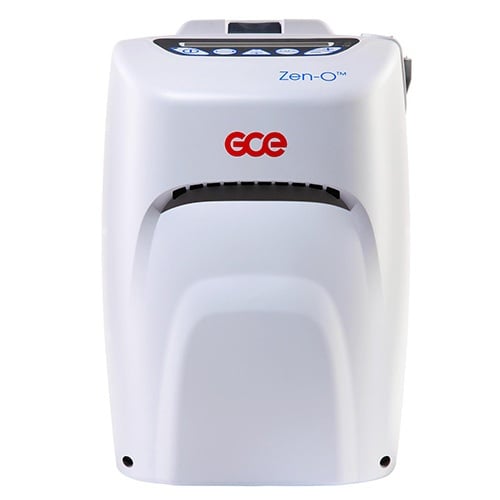

As you can imagine, there are several disadvantages to this. Since the device is working around the clock to administer oxygen, your battery life is going to suffer. Most continuous flow concentrators will only run for a couple of hours before the batteries need to be recharged or replaced. This can really be problematic if you want to get out of the house for an extended period of time in order to visit a friend or take a vacation.

Since continuous flow units are so bulky, taking your oxygen device into public areas or walking up long flights of stairs is out of the question. Unless you’re able to carry the machine on your back, the nasal cannula will dangle down quite a bit which can be a tripping hazard for you and others. To mitigate this risk, some people resort to using mobility aids that they can rest the device on while walking. This way, there’s no chance that the oxygen tubing will get caught on anything. The obvious downside of this is that you’ll have yet another thing to keep track of as you’re out and about.
Pulse Dose Portable Oxygen Concentrators
The final type of oxygen concentrator is a pulse dose portable oxygen concentrator. The term “pulse dose” refers to the way that oxygen is administered to the patient. Rather than being released in a constant stream, the device closely monitors your breathing rate and only delivers oxygen at the optimal moment. What this means is that no oxygen is wasted and you’ll have a lot more battery life to work with. Another major benefit of this technology is that it enables manufacturers to make their devices much lighter and smaller.

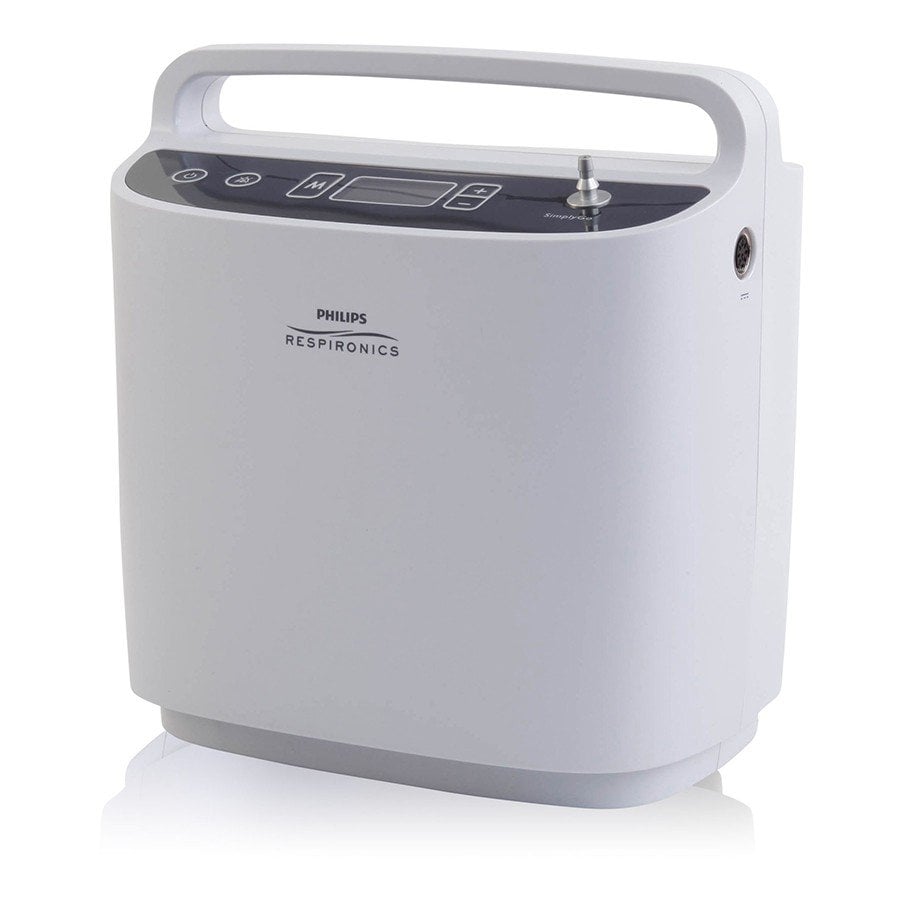
The Caire FreeStyle Comfort is one of the top pulse dose portable oxygen concentrators currently on the market. It weighs in at just 5 pounds and the 16-cell battery lasts up to 8 hours on a setting of 2. It also has a maximum oxygen output of 1,050 ml/min which is more than enough for the vast majority of oxygen patients. The great thing about the FreeStyle Comfort and most other pulse dose POCs is that it’s approved by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) meaning you’ll be able to take it on any commercial airline with you.

Ultimately, using a pulse dose portable oxygen concentrator as opposed to one of the other oxygen devices listed above, you’ll have more freedom to go where you please and spend more time doing the things you love. They’re very simple to use straight out of the box so you don’t have to worry about spending hours reading through the user manual or researching online. There is also a wide range of accessories available for them in order to help you customize and make the most of your new device.
Conclusion
In this post, we took a look at three of the main oxygen devices on the market: oxygen tanks, liquid oxygen tanks, and oxygen concentrators. Each of these devices is widely used by oxygen patients across the world and they are each viable in their own way. However, all things considered, pulse dose portable oxygen concentrators provide some pretty distinct advantages over the other options. Most importantly, they’re extremely lightweight meaning you can take them anywhere in the world with comfort and ease.
{{cta('b59df0c1-c4de-47a8-8e1c-0d33d4b414aa','justifycenter')}}
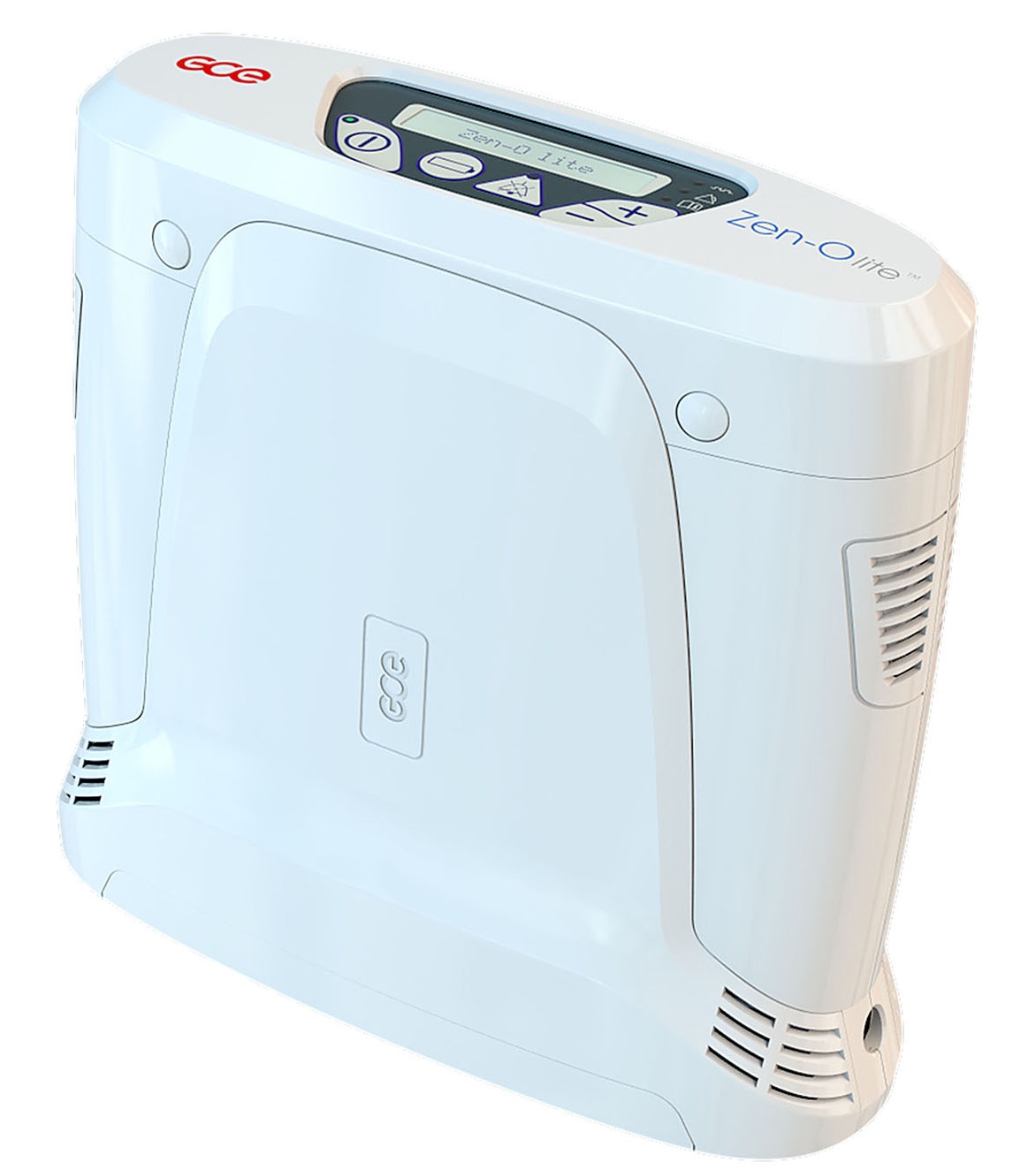
The GCE Zen-O Lite, for example, is a pulse dose portable oxygen concentrator that weighs in at just 5.5 pounds. With both batteries inserted into the device, you’ll get up to 8 hours of battery life on one charge! That’s enough to last you the whole day and then some. It’s also one of the most powerful pulse dose units offering up to 1,050 ml/min (milliliters per minute ) of oxygen on one charge.
There are many incredible pulse dose concentrators on the market, so be sure to contact our respiratory specialists to discover which one is best for you. We’ll walk you through the whole process from choosing a device to choosing a buying option. We’ll even help you collect all the necessary paperwork and assist you with being reimbursed through Medicare or another health insurance company. Give us a call at 1-(800)-946-1201 or email us at info@lptmedical.com to get started.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease. COPD is an umbrella term for diseases like emphysema and chronic bronchitis. COPD comes in stages with stage one being mild and four being the very last stage. There is a need to improve the quality of life and slow down progression into subsequent stages.
To do this, it is imperative that a patient goes through pulmonary rehabilitation. This program arms you with the necessary skills to participate in everyday activities without a struggle by teaching you how to properly exercise and diet among other important aspects.
You will also learn breathing techniques and how to get the most out of your inhalers among other useful tidbits.The result of attending pulmonary rehab is less frequent and shorter periods of hospitalization. Faster recovery after exacerbation has also been noted. The exercise is good for consequent anxiety and depression due to the production of endorphins. The program, if ordered by a doctor will be covered by medical insurance.
{{cta('fa8abc2a-1e88-4fa3-82fd-1cb5b9ed43b2')}}
Exercise

Physical activity can be strenuous for a person with COPD. They will often suffer shortness of breath after a short walk and other simple activities.This is because the disease decreases lung function and weakens respiratory muscles. The program arms the patient with tips on how to exercise successfully.
With time, the patient is able to tolerate more activity that is physical. It is advisable that a patient starts small, then gradually increases the intensity of exercise. A good exercise has three parts: a warm up, conditioning and a cool down. The warm up prepares the body for the impending calorie burn. It also prevents muscle injury and increases range of motion.
The conditioning stage is where the party truly starts. In this stage, cardiovascular exercises like walking, jogging, water aerobics, cycling and jumping rope will be good. The cool down can last five minutes and stretching would be enough to allow the body recovery time.
General exercise guidelines may be followed. Like not exercising less than one and half hours after a meal. It is advisable to exercise in the morning because that is when the body is at its peak. Exercise for twenty minutes a day, three times a week is a good place to start. The patient is advised to exhale twice as often as they inhale through pursed lips.
{{cta('b59df0c1-c4de-47a8-8e1c-0d33d4b414aa','justifycenter')}}
Stop Smoking

It is estimated that 10-15% of smokers will develop COPD. After cessation, the difference can be felt within 24 hours. Improvement on blood pressure and heart rate is significant.
In a year, cardiovascular events are less probable by half. Naturally, lung function declines with age. Smoking heightens the rate. To reduce the progress of COPD into advanced stages, a patient should stay away from the cloud permanently.
This is the number one way to modify the natural course of COPD. Studies have shown that women gain the most from tobacco treatment than men. This is not deterrent though as both parties do enjoy a reduced rate of decline of lung function.
What to Eat

After metabolism, the body gains energy and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is waste. COPD patients use a lot more energy when breathing and therefore need up to ten times more calories in their diet.
A prescribed diet will keep the weight optimal. Too much weight will put pressure on the lungs and respiratory muscles. Too little weight will make the patient frail and weak.
A good diet also helps long term bronchodilators work better and reduces the use of rescue medication. One should take plenty of fluids to keep the mucus thin and easy to cough up. Mucus will block airways and cause exacerbation.
Patients should not overeat and should opt for more frequent and smaller meals instead of the traditional three meals. High fiber foods are also recommended. It is important that a patient exercise sodium control. Before using other salt supplements, they should consult. The same applies to alcohol intake. They should take smaller bites to ease breathing and eat while sitting up.
Arsenal of Information

The quality of life of a COPD patient can be significantly influenced by their self-management capabilities. The only way for patients to manage themselves successfully is to have a lot of information about their condition. The program also avails the same information to family members. This ensures that proper care is taken and exacerbations are attended to appropriately.
Often, sleeping position might affect breathing. This can be quite alarming but after going through the program a patient will know that all they have to do is sleep on their side with the head elevated to keep airflow smooth. Patients are also made aware of trials like those involving use of stem cells to repair damaged lungs.
Support
Living everyday knowing that something as minute as strong cologne might set off an exacerbation and quite possibly death is depressing and soul crashing. It is easy to just curl up and wait for death. In addition to medical support, patients will often need emotional and psychological help. There are many blogs where people post their stories and words of encouragement for those on the same COPD boat.
There are also support groups where one can find solace for the bad days. The pulmonary rehabilitation program will direct the patient to these. They will also connect them with excellent COPD specialists. Support might not heal the disease but it will make them feel a little better.
After a patient has completed the program, it is paramount that they stick to the prescribed diet and exercise schedule. Exercise may be as simple as walking up and down the stairs for ten or twenty minutes every day or taking a walk in the park.
This is the only way to ensure continuation of wellness and long term positive effects. Morbidity and mortality, though still quite pronounced, is pushed further away from the patient’s mind. With pulmonary rehabilitation, a COPD patient can live life without letting the impending doom falter their steps.
When you live with COPD or another chronic respiratory disorder, managing your symptoms and getting enough oxygen is an everyday struggle. You might worry about getting enough supplemental oxygen, or fear that your blood oxygen levels drop too low at times.
But what if there was an easy way to make sure your body is getting enough oxygen any day, any time, from the comfort of your own home? Luckily, all you need is a small, hand-held device called a pulse oximeter, and you can do just that.
A pulse oximeter is a quick, simple, and completely non-invasive home method for testing your blood's oxygen saturation. It's a great way to monitor your symptoms, catch abnormalities, and prevent hypoxia, which happens when your blood oxygen levels fall too low.
Pulse oximeters are not just convenient, but also extraordinarily easy to use. All you have to do is clip the tiny, clam-shell-like probe to the tip of your finger, and you can get an accurate reading of your blood oxygen saturation in seconds.
The best part is, you can check your oxygen saturation levels anytime, anywhere, and as often as you'd like!
In this article we'll show you how a finger tip pulse oximeter can be an invaluable tool for many people with chronic lung or heart conditions. Continue reading to learn more about pulse oximetry, how it works, and how you can benefit from having a pulse oximeter in your home.
{{cta('b59df0c1-c4de-47a8-8e1c-0d33d4b414aa','justifycenter')}}
Do You Need a Pulse Oximeter?

Pulse oximeters can be useful for people suffering from a variety of respiratory and cardiovascular disorders. It can help monitor symptoms of lung disease, asthma, and even some heart-related conditions.
Fingertip pulse oximeters help people with chronic diseases monitor their blood oxygen levels, for example, after a heart attack or in severe cases of COPD. It can help you watch out for hypoxia and alert you when your oxygen saturation is abnormally low so you can seek medical attention immediately.
A pulse oximeter can also be a useful for people who receive supplemental oxygen therapy. It lets you monitor your oxygen saturation levels throughout the day so you know when to use your oxygen and can help you and your doctor ensure that the therapy is adequate and effective.
You might benefit from a pulse oximeter if:
- You Use Supplemental Oxygen
- You have COPD
- You have Asthma
- You have Lung Cancer
- You have Pneumonia
- You have suffered a heart attack or heart failure
{{cta('fa8abc2a-1e88-4fa3-82fd-1cb5b9ed43b2','justifycenter')}}
Why Your Oxygen Saturation is Important

When you breathe, you absorb oxygen gas from the air into your lung tissue, where the oxygen molecules can then enter your bloodstream. From there, your heart pumps the oxygen-rich blood throughout your body to the organs and tissues that need it.
This is the main purpose of your respiratory system: It takes oxygen out of the air and then carries it around the body, where it absorbed and used as fuel to keep your muscles and all the other cells in your body working.
The amount of oxygen in your blood at any given time is known as your blood's oxygen saturation. Oxygen saturation is an important metric to keep track of, because it can tell you a lot about the severity of lung diseases like COPD and what kind of medical treatments or supplemental oxygen therapies patients might need.
The most important thing that your blood oxygen saturation can tell you is whether or not your lungs are functioning well enough to provide your body with enough oxygen. If your blood oxygen saturation is too low, you are in danger of experiencing hypoxia. If it is normal, then you know that you are getting enough oxygen.
How Does a Fingertip Pulse Oximeter Work?

To use a pulse oximeter, all you have to do is clip the device to your finger and press the button. Within a few moments, the device will display your oxygen saturation percentage on its front-facing screen.
You might be wondering, how can a hand-held device accurately read your blood oxygen levels by simply clamping to your finger and without drawing blood? The answer is with a beam of light and a sophisticated light saturation sensor.
Pulse oximeters work by shining a light through your skin which then reflects off the blood flowing through your vessels just underneath. Then the light reflects back off of your blood, back up through your skin, and into the sensitive light saturation sensor.

Based on the saturation of the light that returns, the sensor can tell how much oxygen was in the blood that it reflected off of. That's because hemoglobin, which acts like a transport vehicle for oxygen in your blood, absorbs a lot of light when it's carrying oxygen.
The more light that gets absorbed, the higher your blood oxygen saturation is.
A pulse oximeter reports the results of its readings as a percentage. This number represents what percentage of the hemoglobin molecules in your blood are saturated with oxygen, known as your blood oxygen saturation level.
How Do You Interpret the Results?

Usually an oxygen saturation reading that's anywhere above 95% is considered normal and healthy. However, if you suffer from COPD or another breathing condition, your oxygen saturation might be lower.
You will need to talk to your doctor about what kinds of readings you should expect given your unique disease and physical condition. However, if you get a blood oxygen saturation reading below 90%, you should always seek immediate medical attention unless otherwise directed by your doctor.
While a pulse oximeter can give you a good idea of how well your lungs are functioning, it should never be used as a replacement for regular doctor visits and spirometry tests. You will need to work with your doctor and use your pulse oximeter readings in combination with other lung function tests to accurately monitor and manage your disease.
How You Can Benefit from Using a Home Pulse Oximeter

The great thing about pulse oximeters is that you can get immediate, accurate oxygen saturation readings whenever you need them. You can monitor your blood oxygen levels and watch for abnormal readings without going through any hassle or having to wait until your next visit to the doctor.
If you have a chronic respiratory disease like COPD, you are in regular danger of your blood oxygen levels falling too low. It's important to be aware when this happens because low oxygen saturation can put tremendous strain on your body.
If it goes untreated for long enough, low blood oxygen levels can cause life-threatening complications including pulmonary hypertension, heart disease, and respiratory failure.
That's when having a home pulse oximeter can be a lifesaver. Using a pulse oximeter to test your blood oxygen saturation levels on a regular basis allows you to keep a closer eye on your respiratory health and take a more active role in your own treatment.

The best thing about owning a fingertip pulse oximeter is the peace of mind you get from knowing that you can easily and instantly test your blood oxygen saturation and get an early warning if it falls too low. This gives you the opportunity to use medication and other therapies to bring your oxygen saturation back up to healthy levels, or seek medical attention if it falls too low.
A pulse oximeter can also be a valuable tool to assess your condition if you experience worsened symptoms or exacerbations. It can alert you to when your oxygen saturation is low enough to warrant medical attention, and can be extremely helpful in an emergency situation.
Also, if you use supplemental oxygen to treat COPD or another respiratory disorder, a pulse oximeter is a wonderful tool to have on hand. Checking your oxygen saturation levels throughout the day can help you recognize times when you need to use your supplemental oxygen and increase the accuracy of your oxygen therapy. It can also help you assess whether or not your oxygen flow rate is accurate and if your oxygen therapy is working as effectively as it should.
Overall, having a home pulse oximeter lets you take control of your own disease treatment in a way you never could before.
Here is a list of benefits that a pulse oximeter has to offer:
- The ability to conveniently test your oxygen saturation levels from the comfort of your own home
- The ability to monitor a variety of chronic illnesses, including asthma, COPD, and heart disease
- Testing that is simple, non-invasive, and pain-free
- The ability to more accurately and efficiently use supplemental oxygen to manage your disease
- The ability to test your oxygen saturation as often as you like, any time of the day
- The ability to identify certain activities and times during which your oxygen saturation levels are lower (e.g. while sleeping)
- The ability to monitor your oxygen levels during exercise and use supplemental oxygen accordingly
- Early warning for when your oxygen levels fall dangerously low and you need to seek medical attention
New Innovations in Pulse Oximetry Technology
Simple hand-held pulse oximeters have been used to measure oxygen saturation in homes, hospitals, and doctor's offices for many years. Up until recently, the only type available was the typical simple pulse oximeter that does nothing more than clamp onto your finger and spit out a reading on its screen.
Now, there is a new type of pulse oximeter called a smart pulse oximeter that can do much more than its predecessors. Smart pulse oximeters send your readings to a smartphone app that you can access on your iPhone or Android device to accurately track your oxygen saturation levels every day.
Features Included in Smart Pulse Oximeters

What makes a smart pulse oximeter so useful is that it sends all of the data it collects to an app that helps you better monitor how your readings change over time. And because smart pulse oximeters can measure more than just oxygen saturation, they can help you track other important health data as well.
Smart pulse oximeters can read and display:
- Your blood oxygen saturation levels
- Your pulse rate
- Your perfusion index (a measure of how strong or weak your pulse is)
Having a single app to store and review all of this data can help both you and your doctor better keep track of and utilize your oxygen saturation readings. It is much more convenient and versatile than trying to track all that data by hand, and it's more accurate, too.
Some smart pulse oximeters can even adjust their readings to account for factors like dark skin tone and low perfusion. This allows them to provide more accurate, individualized data for a wide range of different patients and conditions.
Most smart pulse oximeters use a USB cable to export the data from your pulse oximeter device to the app on your smartphone. However, you can now get wireless smart pulse oximeters that use Bluetooth technology to instantly sync the data with your phone.
How to Choose the Right Pulse Oximeter for You
There are a variety of different pulse oximeters, including smart pulse oximeters, out there on the market to choose from. While they used to be quite pricey, there are now many more affordable, inexpensive pulse oximeters you can buy.
However, if you use supplemental oxygen or suffer from severe COPD, it might be worth it to invest in a more sophisticated device. Its' important to make sure your pulse oximeter is durable, accurate, and FDA-approved if you rely on it to monitor your health.
Although a bit more pricey, smart pulse oximeters are a perfect solution if you want to skip the hassle of writing down all your data after every reading you take. Smart pulse oximeters keep a record of every pulse reading all in one place for you, that way it's as easy as possible for you and your doctor to make sense of the results.
How to Get The Most Accurate Readings Possible

Even the best home pulse oximeters have limits and may not be accurate 100 percent of the time. However, if you use your pulse oximeter correctly and understand which factors can throw its measurements off, you can depend on your pulse oximeter to give you useful readings the vast majority of the time.
Know these following factors that can cause your pulse oximeter to give an inaccurate reading:
- Taking the reading in cold weather or having very cold hands
- Certain colors of nail polish (blue, black, or green nail polish can throw off a pulse oximeter's light spectrum sensor)
- Poor circulations in your fingertips (you can usually remedy this by rubbing your hands together for a couple of minutes to get your blood flowing)
- Medical dyes injected into your bloodstream
- Dark skin pigmentation (Talk to your doctor to make sure that your pulse oximeter is correctly calibrated for your skin type so you can be sure your readings are accurate.)
You should also be aware that certain serious medical conditions can also affect a pulse oximeter's sensors and give you an inaccurate reading. These conditions include cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, arrhythmia, shock, edema, carbon monoxide poisoning, and arteriovenous fistulas.
As long as you keep these caveats in mind, you should always be able to get accurate, reliable readings from your pulse oximeter. However, it's still important to see your doctor and get regular lung function tests to get a more complete and accurate assessment of your condition.
Get Your Own Home Pulse Oximeter Today
If you have a chronic lung disease like COPD, getting your own home pulse oximeter can be an effective way to take back some control in your life and get some extra peace of mind. It can help you monitor your disease, warn you when your oxygen levels drop too low, and even help you use supplemental oxygen more effectively.
If you think that a home pulse oximeter could help you, talk to your doctor to learn how you can benefit from monitoring your blood oxygen saturation at home. Your doctor can also show you how to use your pulse oximeter correctly and accurately interpret your results.
Home pulse oximeters have become an invaluable tool for people with COPD and other chronic conditions to track their respiratory health, and it's one of the best ways get the most out of supplemental oxygen therapy.
Pulse oximeters are convenient, effective, inexpensive, and can significantly reduce the worry and burden of living with a variety of chronic conditions. So don't keep yourself in the dark any longer, and look into getting your own home pulse oximeter today!
Although COPD is known primarily as a lung disease, some of its most serious complications have to do with the heart. People with COPD tend to struggle with a variety of cardiovascular symptoms and complications, including cardiovascular disease, heart attacks, and heart failure.
Heart disease is the number one cause of death in the US, and is also one of the most common killers of people with COPD. However, the risk of heart attacks and heart failure for COPD patients is significantly higher than it is in the general population, even in patients who don't have other heart problems.
Because of this, keeping your heart and cardiovascular system healthy is a critical part of COPD treatment. Keeping your heart strong can actually reduce COPD symptoms as well as prevent serious, life-threatening complications like heart attacks.
In this article, we're going to explain how COPD affects the heart and why the disease raises your risk of having a heart attack. We'll also show you what you can do to prevent heart attacks and keep your heart healthy with COPD.
{{cta('b59df0c1-c4de-47a8-8e1c-0d33d4b414aa','justifycenter')}}
Symptoms of a Heart Attack

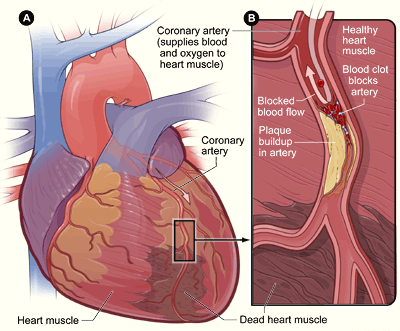
A heart attack happens when your blood vessels become so narrowed that it cuts off blood flow to the heart. This can happen as a result of a blood clot, high blood pressure, and clogged arteries, which are often the result of heart disease.
Doctors and researchers don't fully understand exactly why many heart attacks happen, or through what exact mechanism COPD causes sudden heart attacks. However, they do understand the major risk factors, which include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, stress, and diabetes.
The earlier you get treatment for a heart attack, the more likely you are to survive and avoid serious, permanent damage to your heart. Because of this, it's very important to know the symptoms of a heart attack and how to recognize them, especially if you have COPD.
However, heart attacks don't feel the same for every person and the symptoms can vary widely from case to case. Some people experience severe chest pain or fainting, while some feel little pain or hardly any symptoms at all.
Some heart attacks happen suddenly, with little warning and few symptoms, but some develop slowly over the course of hours, days, or weeks. The most reliable symptom to look for is chest pain, especially chest pain that gets worse with activity and gets better with rest.
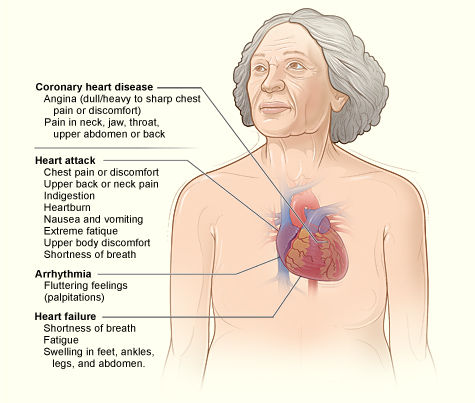
Here are some of the most common symptoms of a heart attack:
- Chest pain that may feel like any of the following: pressure, tightness, squeezing, or aching.
- Chest pain that spreads to your arm, neck, jaw, or back.
- Heartburn
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Shortness of breath
- Sudden dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Cold sweating
- Fatigue
If you notice the symptoms of a heart attack, you should seek medical attention immediately. Have someone drive you to an emergency room or call 911 right away.
Don't ever ignore the warning signs of a heart attack; it's better to get checked by a doctor—even if it might be nothing—than to wait too long and risk suffering severe heart damage or death. Getting to an emergency room at the first sign of a heart attack will give you the greatest chance of recovery.
{{cta('fa8abc2a-1e88-4fa3-82fd-1cb5b9ed43b2','justifycenter')}}
How COPD Raises Heart Attack Risk
People with COPD tend to get heart disease earlier and are more likely to suffer heart failure and die from cardiovascular problems. Even COPD patients who don't have cardiovascular disease or other heart complications have a much higher risk of sudden cardiac death.
According to one study, living with COPD more than doubles your risk of sudden cardiac death, and the risk gets even higher for patients who have worse COPD symptoms and complications. Because of this, researchers are beginning to consider COPD an independent risk factor for heart disease and heart attacks, akin to high blood pressure and diabetes.
To understand why COPD causes heart attacks, you have to understand how the disease affects the cardiovascular system, including the heart, blood vessels, and pulmonary arteries (blood vessels in the lungs). These critical organs and tissues sustain damage over time as your body is affected by COPD, eventually leading to complications like cardiovascular disease, heart attacks, and heart failure.
The Heart-Lung Connection

Heart disease is a leading cause of death for all people in the US, not just people with COPD. However, COPD patients' heart problems are directly tied to their disease, which damages the heart in a specific way.
To understand how COPD causes heart problems, you have to first understand how the function of heart and lungs are intimately and inextricably linked. The heart and lungs work together in synchrony to supply your body with oxygen and remove waste, like carbon dioxide, from you body's tissues. If either organ is damaged, the other organ, and the whole cardiovascular-respiratory system, suffers too.
In fact, it's hard to overstate how much the heart and lungs rely on one another to function. The heart takes in oxygen-poor blood from the body and pumps it straight into the lungs to become oxygenated again. As the blood travels through the pulmonary arterties (blood vessels in the lungs), it absorbs oxygen and goes right back into the heart, where it pumps the now-oxygen-rich blood back throughout the body.
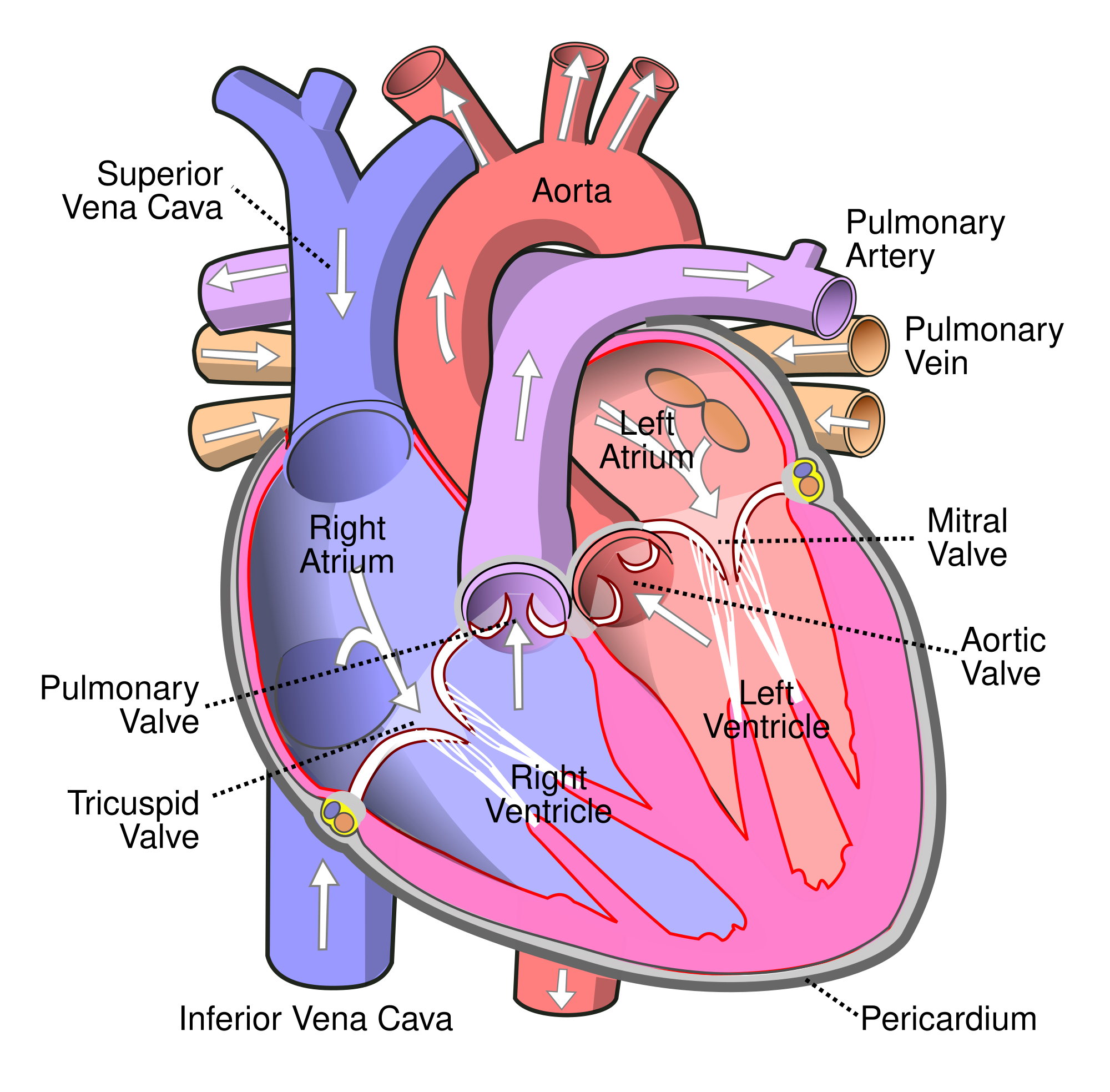
But in order to absorb oxygen, your blood must pass through the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in your lungs that allow oxygen to pass from the air into your blood. However, people with COPD have many damaged, non-functioning alveoli, so they aren't able to absorb as much oxygen as healthy lungs can.
COPD also causes inflammation in the lungs, which further damages alveoli and reduces the lung's ability to absorb oxygen even more. Eventually, lung function declines so much that the blood that passes through the pulmonary arteries doesn't get fully oxygenated, resulting in low blood oxygen saturation levels (a condition known as hypoxemia).
How COPD Strains the Cardio-Respiratory System

The main problem that people with COPD have is that their lung function is severely limited. Damaged air sacs and airway obstruction makes it difficult for the lungs to absorb enough oxygen causing serious respiratory symptoms and hypoxemia.
Hypoxemia is very bad for your body, and the heart tries to compensate for the low blood oxygen levels by pumping faster and harder. This increases the blood pressure in your lungs, which in turn creates extra back-pressure on the heart as it tries to squeeze extra blood into the pulmonary arteries.
Over time, the back-pressure that it puts on the heart causes the heart to swell and enlarge. This makes the heart walls weaker and makes it even more difficult for your heart to pump blood. These lung problems get worse and worse over time, all the while putting more and more strain and pressure on the heart.
This cycle continues, and, over time, makes your heart larger, weaker, and less effective at pumping blood through your body. As your COPD gets more severe, so does the strain on your heart, which significantly increases your risk for heart attacks and heart failure.
Pulmonary hypertension can also happen when blood vessels in the lung become narrowed and stiffened, as a result of airway obstruction caused by COPD. This also causes high blood pressure in the lungs and creates back-pressure in the heart every time it tries to pump blood into the pulmonary arteries.
Over time, this enlarges and weakens the heart, making it more and more difficult to pump blood through the lungs. If the heart becomes too weak and enlarged, it can fail, causing right-sided heart failure.
COPD and Cardiovascular Disease
Recent studies have shown that cardiovascular disease is much more common in people with COPD than was once believed. Researchers believe that this may be directly related to inflammation rather than breathing problems related to COPD.
COPD causes chronic inflammation throughout the body, not just in your lungs. One of the places this inflammation does the most damage is in the arteries, where it leads to plaque build-up and cardiovascular disease.

Beacause of this, inflammation is another major factor contributing to the increased incidence of cardiovascular disease in COPD patients. Cardiovascular disease includes high blood pressure, stroke, heart disease, coronary artery disease, and artherosclerosis.
How to Reduce Your Risk of Heart Attacks and Heart Failure if You Have COPD
Now that you understand how COPD causes heart attacks and cardiovascular complications, you need to know how to protect your heart from the strain caused by the disease. Luckily, there are plenty of things you can do in your everyday life to strengthen your heart and improve your cardiovascular health.
In this next section, we'll show you how to make heart-healthy choices and reduce your risk of having a heart attack if you have COPD. We'll give you a variety of tips and techniques for reducing your risk of COPD-related heart complications including how to monitor your blood oxygen, eat a heart healthy diet, and how to exercise for a healthy heart.
Stop Smoking

A history of smoking is a major link in the relationship between COPD and heart attacks. In fact, people who smoke are up twice as likely to suffer a heart attack compared to non-smokers.
Smoking also leads to high blood pressure and significantly increases your risk for cardiovascular disease. It also affects the balance of cholesterol in your blood and causes plaque to build up in your arteries.
That's not even mentioning the devastating effect that smoking has on your lungs, especially when you already suffer from COPD. Smoking will worsen your symptoms, increase your risk of having COPD exacerbations, and lead to quicker lung function decline.
If you need help to quit smoking, talk to your doctor about quit-smoking medications or programs in your area. You can also visit the CDC's website for a variety of quit-smoking materials and links to smoking cessation guides from the American Lung Association, American Heart Association, and the American Cancer Society.
Prevent COPD Exacerbations

Exacerbations are a major cause of heart attacks in people with the COPD. In fact, experiencing an exacerbation can significantly increase your risk of a heart attack for days or even weeks after after you recover.
One study showed that a patient's heart attack risk is more than doubled for up to five days after an exacerbation. This likely happens because exacerbations cause an increase in a variety of COPD symptoms responsible for putting extra strain on the heart.
Increased respiratory symptoms experienced during an exacerbation, like worsened airway obstruction and shortness of breath, can lead to hypoxemia and put a great deal of pressure on the heart. Exacerbations also tend to increase inflammation in the body, including the blood vessels, which can worsen cardiovascular disease and raises your risk of heart attack.
Exacerbations are also very difficult to recover from, and in some cases results result in a permanent worsening of COPD symptoms. This is bad for both your heart and lungs. By reducing the number of exacerbations you experience, you may be able to preserve your lung function longer and prevent permanent increases in the level of strain that the disease puts on your heart.
Other studies have shown that respiratory infections can increase heart attack risk even in people who don't have COPD. One study found that people who have experienced heart attacks in the past are up to seventeen times more likely to have a heart attack within a week following recovery from a respiratory infection.
This shows how serious of an effect respiratory problems can have on the heart in the short term, and highlights why it's so important for people with COPD to minimize their symptoms and avoid getting sick. Even a minor respiratory illness can cause exacerbations and make COPD symptoms much worse, which can quickly lead to life-threatening events like respiratory failure or a heart attack.
Exacerbations are usually caused by respiratory illnesses and infections, but they can also be caused by exposure to respiratory irritants like allergens and air pollution.

Here are some more tips for preventing COPD exacerbations and heart attacks:
- Too much mucus in your lungs and airways can trap bacteria and cause you to get sick. To prevent mucus build-up and reduce airway obstruction, use airway clearance techniques to move the mucus up and out of your lungs and airways.
- Avoid spending time with or near anyone who is sick, including children. Whenever possible, stay away from sick people's homes and belongings until they have fully recovered.
- Protect yourself from germs when you're out in public places. Wash your hands after touching public surfaces and carry hand sanitizer with you for when you can't use a sink.
- Avoid going to crowded places during the winter months when many contagious illnesses spread. Try to schedule visits to museums, convention centers, concerts, and sporting events outside of cold and flu season or go when they are less crowded.
- Protect your lungs from respiratory irritants like pollution, allergens, dust, and mold. They can cause exacerbations, worsen inflammation, and make your symptoms worse.
- Daily symptom management is key for preventing COPD exacerbations. Make sure you follow your COPD treatment plan carefully and take your medications as prescribed every day in order to keep your symptoms under control.
Make Exercise a Priority

Getting regular physical activity every week is an essential part of keeping your heart and cardiovascular system strong. It also helps strengthen your muscles and increase your endurance, which can improve your mobility and allow you to live a fulfilling, active life with COPD.
Exercise strengthens your heart in many ways, including by reducing blood pressure, improving blood circulation, and reducing stress and anxiety. It can also prevent strain on your heart caused by hypoxemia by strengthening your breathing muscles and helping your body use oxygen more efficiently.
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends that you get at least thirty minutes of exercise five days a week for a healthy heart. It doesn't matter much whether you do thirty minutes all at once, or break it up into a few ten-minute sessions to do throughout the day.
However, getting daily exercise doesn't mean that you have to join a gym or start lifting heavy weights. Even just walking, doing aerobics, or doing basic body weight or chair exercises is usually enough to stay in shape.
The most important thing is to do what you can manage and get moving right away. Even if you can't meet the AHA's guidelines, getting some activity is always better than getting none.
For example, studies show that walking as little as thirty minutes a day can reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease by 18% and reduce your risk of heart attack by 35%. Some studies even show that walking is just as effective as running or jogging for preventing high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease.
COPD can make it difficult to exercise, but having the disease makes it more vital than ever to get more physical activity. It's necessary for your lungs, your heart, your overall health, and for maintaining your mobility and quality of life.
If you struggle with exercise because of severe shortness of breath or other COPD symptoms, talk to your doctor for advice. He might be able to recommend activities or exercises classes tailored to your ability level or refer you to a pulmonary rehabilitation class.
Monitor Your Blood Oxygen With a Pulse Oximeter

As we discussed earlier, people with COPD are particularly prone to experiencing hypoxemia, or low oxygen saturation levels in their blood. This happens when your lungs aren't able to absorb enough oxygen, and tends to occur most often during exercise, bouts of breathlessness, exacerbations, and during sleep.
Hypoxemia puts extra strain on both your heart and lungs and can lead to a variety of serious complications over time. That's why many COPD patients use supplemental oxygen; by providing concentrated oxygen to their lungs, it allows them to absorb more oxygen and prevent their blood oxygen saturation levels from falling too low.
One problem with preventing hypoxemia and using supplemental oxygen is that it can be difficult to know when your blood oxygen saturation falls below normal levels. Watching out for the external signs and symptoms of hypoxemia, like breathlessness and fatigue, is important, but they can be difficult to catch, especially if you experience chronic COPD symptoms every day.
Luckily, there's an easy, cheap solution for keeping an eye on your blood oxygen saturation levels and preventing hypoxemia: a home pulse oximeter. It's a small, non-invasive device that can read your blood oxygen levels by shining an infrared light through your skin.
Pulse oximeters are extremely simple to operate and can be used to check your blood oxygen saturation over and over. It takes only a few seconds to take a reading which makes it a great way to monitor yourself for hypoxemia throughout the day, especially when you sleep, exercise, or feel short of breath.
Your pulse oximeter can also help you learn when to use your supplemental oxygen if you've been prescribed oxygen therapy during the day. It can also give you an early warning of severe hypoxia, a medical emergency that occurs when your blood oxygen levels fall so low that it starves your organs of oxygen.
If you suffer from COPD-related heart problems, a home pulse oximeter can be an invaluable tool for monitoring your heart health and preventing heart attacks. By helping you keep your blood oxygen saturation at a healthy level and warning you when it drops too low, having a personal pulse oximeter could even save your life.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation

Pulmonary rehabilitation is a type of special class designed specifically for people who have COPD and other respiratory diseases. It's a solution recommended often to patients who struggle with a variety of aspects related to their health and managing COPD, including those struggling with heart problems.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is one of the best ways to learn all about how to manage your symptoms and overcome all the different challenges of living with COPD. It's kind of like a variety show that covers all kinds of different, yet related, topics, except each class focuses on a different aspect of living with a respiratory disease.
Through pulmonary rehabilitation, you can practice and build up the skills that can help you keep your heart strong and prevent other COPD complications. Most courses cover most or all of the techniques for heart health that we will discussed in this article, including exercise, breathing techniques, stress management strategies, and proper medication use.
Pulmonary rehabilitation also helps you build the skills needed to keep your heart healthy and stave off COPD-related heart complications like heart attacks and cardiovascular disease. In fact, pulmonary rehabilitation is often referred to as “cardiac and pulmonary rehabilitation” and is often recommended to people who have suffered cardiac events like heart attacks or heart failure.
Attending a pulmonary rehabilitation class is also great opportunity to learn from and ask questions to a variety of medical professionals who are knowledgeable about COPD. You'll also get to meet other COPD patients and the chance to get social and emotional support from your peers.
If you have trouble managing your disease or suffer from COPD-related heart problems, talk to your doctor about enrolling in pulmonary rehabilitation. You will need a referral from your doctor since classes are often in high demand and can sometimes be difficult to get into.
Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet

.png)
Activities of daily living (ADL) is a term that was first coined by Sidney Katz in 1950. Essentially, it refers to the basic functions that an individual must perform on a daily basis in order to be considered self-sufficient. By better understanding the level of independence of patients with debilitating illnesses like COPD, osteoporosis, or Alzheimer’s Disease, medical professionals are able to make better decisions for their patient’s well-being such as recommending medical equipment or an assisted living facility. Activities of daily living are generally divided into five distinct categories:
Personal Hygiene - bathing, grooming, hair care, and oral health
Continence - using the bathroom
Dressing - the ability to select clothing and dress for different occasions
Feeding - the ability to eat and drink
Ambulating - the ability to walk and move around independently
When it comes to managing your daily life with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), it’s very important to consider how your condition affects your ability to live independently. Studies have shown that ADLs can be very challenging for respiratory patients because they can lead to dyspnea (shortness of breath) and oxygen desaturation, meaning the percentage of oxygen in the blood is lower than what it should be.
{{cta('fa8abc2a-1e88-4fa3-82fd-1cb5b9ed43b2','justifycenter')}}
In this post, we’ll take a look at the importance of supplemental oxygen for carrying out activities of daily living. We’ll also show you why portable oxygen concentrators are the best device to use for maintaining your freedom and independence. If you have any questions about these units, please feel free to leave a comment or reach out to our respiratory specialists.
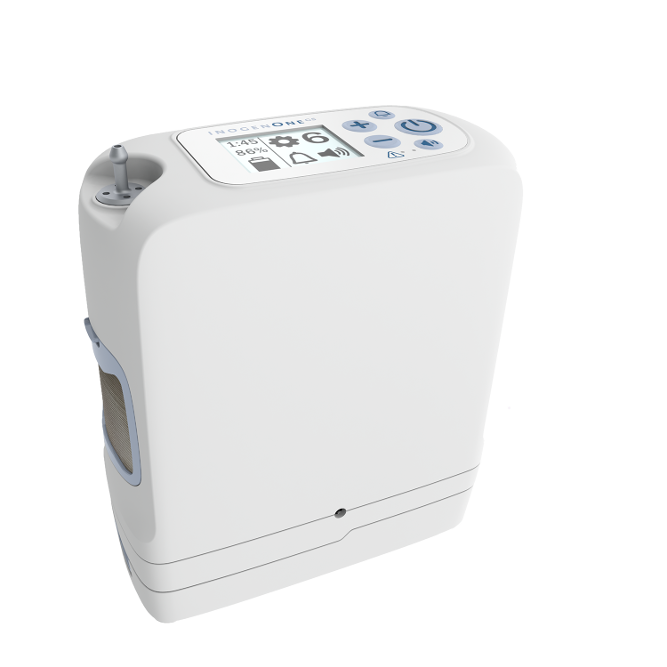
What is a Portable Oxygen Concentrator?
A portable oxygen concentrator is an electronic device used to administer medical-grade oxygen. POCs are the most state-of-the-art oxygen units on the market because they’re extremely lightweight and versatile. Using a POC, you’ll be able to go more places and do more things than if you had a standard compressed oxygen tank or liquid oxygen tank. Since they’re electronic devices, you simply need to have access to a source of power in order to recharge your batteries. You’ll never have the need to reach out to an oxygen company ever again to refill or deliver new tanks to your home!

One of the greatest benefits of owning a portable oxygen concentrator is that they’re approved by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) for in-flight use. What this means is that you can take your POC with you on any commercial flight within the United States. This is a freedom that COPD patients never had in the past because compressed oxygen tanks and liquid oxygen tanks are not allowed on flights for safety reasons. Upgrading your old outdated oxygen device to a portable oxygen concentrator quite literally opens up a world of possibilities! Without further ado, let’s take a look at why activities of daily living are so much easier when you have a portable oxygen concentrator.
Reduced Shortness of Breath
The human body has a complex system for managing breathing rate and breathing depth. Breathing is part of something called the autonomic nervous system which regulates involuntary physiologic processes like heart rate and blood pressure. However, you also have the ability to take control of your lungs through voluntary breathing. Exercises like deep breathing or controlled breathing are great for teaching you how to use your lungs more effectively.
![]()
One of the primary factors that affect respiratory rate is how much carbon dioxide is in the blood. When you are unable to expel air from the lungs fully — a problem that’s common among COPD patients — CO2 begins to build up in the bloodstream. This change in CO2 levels is detected by chemoreceptors which send a message to the medulla oblongata (the control center for the lungs) to increase respiratory rate. Other factors that affect respiratory rate and depth include atmospheric pressure, intra-alveolar pressure, and body temperature.
If you have COPD, interstitial lung disease, or any number of other respiratory conditions, the best way to reduce feelings of breathlessness is by increasing the concentration of oxygen in the lungs. By doing so, you will stabilize CO2 levels in your blood and the chemoreceptors will never send a message to your brain that you need to breathe quicker or more heavily. What this means when it comes to activities of daily living is that you won’t need to stop to catch your breath so frequently.

Using a portable oxygen concentrator throughout the day will prevent you from becoming breathless and thus reducing your chance of experience a COPD exacerbation. Many people find it difficult to keep up with their friends or loved ones because they need to stop to rest frequently. But with a portable oxygen concentrator, you can easily adjust the amount of oxygen you’re receiving based on how you’re feeling. It’s important to speak with your doctor, however, who will tell you what oxygen levels are acceptable.
Improved Mental Alertness
Your ability to complete daily tasks like eating, bathing, and cooking is equally reliant on your mental ability as it is your physical ability. When the oxygen levels in your blood are low this may result in brain hypoxia, also known as cerebral hypoxia, or low oxygen levels in the brain. Symptoms of brain hypoxia include temporary memory loss, impaired motor functions, confusion, lightheadedness, and more.
![]()
Maintaining a “sharp” mind with age is notoriously difficult and living with a respiratory condition like COPD can make it even more challenging. However, by carrying a portable oxygen concentrator with you wherever you go and keeping your oxygen saturation at a healthy level, you’ll be able to rule out one potential cause of cognitive decline as you go about your daily life. Studies have found that there is a correlation between disease severity and cognitive decline, so the more you can do to slow the progress of COPD, the better off you will be in terms of your mental health as well.
A portable oxygen concentrator will provide you with a convenient and reliable source of oxygen as you go about your day. POCs like the Inogen One G5 and Caire FreeStyle Comfort simply need to be turned on and then you can adjust the flow setting however you need it. Then all you need to do is set it and forget it. Your POC will provide you with a steady supply of oxygen all day allowing you to go about your day with your oxygen needs out of mind. This will afford you the freedom to focus your attention on what you’re trying to accomplish rather than worrying about whether your needs are met.
{{cta('b59df0c1-c4de-47a8-8e1c-0d33d4b414aa','justifycenter')}}
Another reason mental alertness is so important is for your safety. People experiencing cognitive decline, more specifically dementia, are at a higher risk of experiencing a fall. Like we discussed in a previous blog post, experiencing a fall, whether it’s inside or outside your home can be dangerous. Studies have also found that dementia patients are at a greater risk for car accidents. Whether you’re driving to the store or just doing chores around the house, maintaining your oxygen levels will keep your mind sharp so that you can navigate safely.
Improved Exercise Tolerance
As you’re likely already aware, a healthy exercise routine is paramount to any COPD treatment plan. While exercise is important for everyone, it’s especially important for people with chronic lung conditions who need their lungs to perform as optimally as possible. Studies show that exercise increases the strength and function of muscles meaning that they require less oxygen. In other words, any form of exercise will benefit you in the long run. But if you want the best exercise routine, speak with your doctor about pulmonary rehabilitation. This is a type of exercise routine that focuses on your lungs and respiratory system as a whole.

When you’re exercising, the rate and depth of your breathing increase because your muscles need more oxygen. What’s more, your heart rate and blood flow increase in order to get that oxygen to the parts of the body that are being worked the most. Not only do your muscles need this oxygen in order to provide them with energy, but oxygenated muscles tend to recover and rebuild faster than muscles that do not get oxygen. So your body will feel more prepared to go through a strenuous exercise the next day.
.png)
Without a doubt, portable oxygen concentrators are the best oxygen device for exercising. Most pulse dose concentrators weigh around 5 pounds and are no bigger than a handbag or purse, so taking one with you when you do your exercise routine is hassle-free. Concentrators like the Caire FreeStyle Comfort also have a lot of carrying options available for them so you can find one that works best for the type of workout you’re doing. The custom carrying case, for example, is great for walking or hiking, but if you’re doing something more involved like weight lifting, you might want to go for the FreeStyle Comfort backpack.
Improved Mobility
Mobility is oftentimes one of the most discussed issues when it comes to aging, and for good reason. The older we get, the more likely we are to suffer from debilitating conditions like osteoporosis, arthritis, impaired strength or balance, or dementia. COPD only makes these conditions worse by adding breathlessness, chest pain, and chronic fatigue to the mix. Sometimes, there isn’t one particular way of dealing with these issues, but instead, COPD patients should work with their doctor and loved ones to find the best solution for them.
![]()
While portable oxygen concentrators certainly don’t “solve” mobility issues, they can definitely help. Old outdated oxygen devices like oxygen tanks are extremely heavy and awkwardly shaped making it nearly impossible to navigate your home with ease. But when you upgrade to a POC, you’ll have a machine that you can carry around the house all day while completing chores and never feeling the need to set it down for a rest. If you use a mobility aid like a walker, wheelchair, or electric wheelchair, you can easily set your POC on your mobility for even more convenience and comfort.

Another benefit of having a portable oxygen concentrator is that it’s easier to prevent your oxygen tubing from getting tangled or tripping over it as you walk. Whether you carry your POC on your shoulder or your back, you won’t need to use long oxygen tubing. But since oxygen tanks are so heavy, you’ll need to use a rolling cart, meaning you’ll need to use much longer oxygen tubing. Many people find that their oxygen tubing gets tangled and wrapped around things while using an oxygen tank which is not only frustrating but dangerous as well.
Conclusion
Activities of daily living are essential tasks that we need to perform each day in order to be independent. If COPD prevents you from doing one or more of these tasks, then you may need to consider hiring a part-time or full-time caretaker. Alternatively, you could invest in a medical oxygen device like a portable oxygen concentrator which allows you to extend your freedom and independence. Many COPD patients feel like they’re taken back in time when they get their first POC because they are able to do things they never thought would be possible after being diagnosed with COPD.
One important thing to note is that oxygen is a controlled substance in the United States. In other words, you will need to have a prescription for medical oxygen from your doctor in order to purchase a portable oxygen concentrator. Whether you have a prescription or not, your best course of action is to give our respiratory specialists a call here at LPT Medical. If you don’t have the required paperwork to purchase a POC, we can reach out to your doctor for you. We’ll also walk you through the process of choosing a portable oxygen concentrator from start to finish. We’re also happy to announce that we now offer assistance with Medicare and medical financing so you can save as much money as possible on a new, used, or refurbished unit.
Give us a call or email us today for more information!
So, you've been diagnosed with a respiratory disease and your doctor says that you need supplemental oxygen in order to breathe better and stay healthy. After considering different options, you and your doctor now decide that a portable oxygen concentrator is the best piece of equipment to fit your needs. Now what?
Oxygen equipment can get pricey, so the first question you probably have is, “are portable oxygen concentrators covered by Medicare?” This is one of the most common questions we get asked, and, unfortunately, it's not an easy one to answer.
The simple answer is that, yes, it is possible to get Medicare and some insurance providers to cover part of the cost of a portable oxygen concentrator. But it's extremely unlikely to happen, and you have to know the whole story to understand why.
Why Insurance Doesn't Like to Cover Portable Oxygen Concentrators
 |
| Image courtesy of Franchise Opportunities |
There are some very rare situations in which Medicare or insurance will cover the purchase or rental of a portable oxygen concentrator. However, even if they do, they don't cover the entire cost of the machine, you have to meet strict criteria to qualify, and each situation is evaluated on a case-by-case basis.
Medical insurance companies have a long reputation of finding any excuse to deny patients coverage for medical equipment and treatments. Unfortunately, Medicare is no exception. They have strict rules that make getting coverage difficult and burdensome, and they often find reasons to deny approval for a treatment even when a doctor says that it's the best option.
That's why, if you want the best possible chance of getting insurance or Medicare to pay for your equipment, you need to understand your provider's criteria. It's important to follow their guidelines meticulously, making sure you dot every “i” and cross every “t” to avoid getting rejected on a technicality.
{{cta('fa8abc2a-1e88-4fa3-82fd-1cb5b9ed43b2','justifycenter')}}
Medicare oxygen benefits can technically be used to rent a portable oxygen concentrator, but the problem is finding a Medicare supplier that offers them. Medicare reimbursement simply doesn't pay suppliers enough every month for them to be able to afford to offer portable oxygen concentrators. Because of this, most people have narrow options for supplemental oxygen and have to choose between either liquid or gas tanks.
 |
| Image courtesy of 401k Calculator |
Other insurance companies, on the other hand, work differently. You will need to talk to your insurance provider to understand what kinds of oxygen supplies they cover and what requirements you need to meet in order to qualify.
Additionally, Medicare and private insurance companies usually require you to prove that you need portable oxygen, specifically, before they will consider covering the cost of a portable oxygen concentrator. This can be a difficult standard to prove, and varies between different insurance providers.
It's important to understand that, even if you find a provider that offers them, you're not likely to get the brand or type of portable oxygen concentrator that you want. Suppliers that offer portable oxygen concentrator rentals usually only carry a small selection, and there's no guarantee that you'll get a high-quality model.
What is Medicare's Criteria for Covering Oxygen Equipment?
Most insurance and Medicare providers will help you pay for some kind of portable oxygen equipment if you meet a specific set of criteria. Usually, this includes a doctor's recommendation and a thorough medical report that proves that you need supplemental oxygen to stay healthy.
Here is an example of Medicare's criteria for covering supplemental oxygen and related equipment:
-
You have a serious lung disease (such as COPD, cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, etc.), or you have symptoms of low blood oxygen levels (such as pulmonary hypertension, erythrocythemia, congestive heart failure, etc.)
-
Your health is likely to improve with supplemental oxygen therapy
-
You have medical tests from your doctor to prove that you have low blood oxygen levels (and these tests were taken while your condition was stable, e.g. not during an exacerbation)
-
You have tried other medications and treatments, but are still unable to get enough oxygen
- You need oxygen therapy 24/7 (Medicare will not cover supplemental oxygen therapy if you only need to use it at night)
All of these criteria have to be verified by your doctor in writing before you can receive Medicare benefits for supplemental oxygen. Your doctor will also have to write and submit a detailed report of your oxygen needs, called a Certificate of Medical Necessity.
If you forget to include any required tests or paperwork, your provider will likely deny or delay your coverage. Therefore, it pays to be meticulous.

Look out for these common mistakes patients make when submitting their Medicare requests:
- Forgetting to include a detailed certificate of medical necessity written by your doctor
- Outdated test results, doctor's examinations, or certificate of medical necessity
- Missing appropriate medical tests proving low blood oxygen levels (hypoxia), such as an arterial blood gas test or oximetry test
- Missing mobility certification (to prove portable oxygen needs)
- Forgetting to include your oxygen prescription
What makes Medicare coverage even more complicated is the fact that Medicare oxygen benefits work on a 5-year cycle. This cycle begins the first time you get coverage for any supplemental oxygen supplies and starts over every five years.
The only time that Medicare will pay enough to purchase or rent new oxygen supplies is during the first three years, when they offer a higher monthly allowance. During the fourth and fifth years, however, the monthly allowance is much lower and only covers the cost of maintenance and care for the equipment you already have.
In order to even have chance at getting a portable oxygen concentrator from a Medicare supplier, you have to get the timing right. If you are already receiving oxygen tanks or other supplies through Medicare, you'll need to wait for the beginning of the next five-year cycle before any Medicare supplier will consider your request for a portable concentrator.
That's why it's important to sign up at the very beginning of the five-year cycle, that way your portable oxygen concentrator supplier can utilize the full amount of your Medicare benefits. Even then, if you do everything right, finding a supplier that offers portable concentrators near you and getting the supplies you want can be next to impossible.
The Trouble With Medicare Reimbursement: Monthly Rentals and Budget Cuts

The unfortunate truth is that, no, most Medicare and insurance providers will not help you pay for a portable oxygen concentrator. Even if your provider agrees to pay for your supplemental oxygen supplies, they will usually only offer enough to cover “cheaper” options like portable liquid or gas oxygen tanks.
These portable tanks are usually cheaper than portable oxygen concentrators in the short run, because the monthly fee to rent the tanks and equipment is relatively small. Most insurance and Medicare providers pay just enough to cover this monthly cost.
Unfortunately, what Medicare offers is usually just not enough on its own for suppliers to afford to give patients portable oxygen concentrators. Medicare pays for all oxygen supplies through a set monthly allowance, which, most of the time, is much too little for such a high-tech device. Because of this, most Medicare oxygen suppliers don't offer portable oxygen concentrators at all.
Even if both you and your doctor think that you need a portable concentrator, Medicare is only required to provide you with a supplemental oxygen supply that's adequate, not the oxygen supply that's right for you. Since that requirement can be satisfied with liquid and gas oxygen tanks, that's often the only Medicare-covered option available.
This is unfortunate, especially because renting oxygen tanks can end up costing more in the long run. The price of renting tanks month after month can quickly add up and be even more expensive than the one-time cost of purchasing a portable oxygen concentrator.
Unfortunately, Medicare and insurance providers tend to think more about short-term costs than long-term ones, and would rather collect the monthly payments for years than pay off a portable oxygen concentrator all at once. Even if you managed to find a provider that offers portable concentrators, the likelihood of getting the brand and model you want is slim to none.
Medicare reimbursement has gotten even worse since it started using the competitive bidding process as a cost-saving strategy. Competitive bidding means that Medicare licenses are only given out to medical equipment suppliers that offer lowest prices.
This results in Medicare offering even less money to pay for oxygen supplies, making it even more impossible for Medicare suppliers to afford to offer portable oxygen concentrators to patients.
But don't be disheartened! Even if your insurance or Medicare won't help you pay for a portable oxygen concentrator, there are other affordable options. Here at Life PT Medical, you can get discounted equipment and financing so you can afford a portable oxygen concentrator without dealing with insurance or Medicare at all.
{{cta('43b79c5e-6bd6-4f02-ac27-2d038d20c146','justifycenter')}}
Solution #1: We Can Offer You the Cheapest Portable Oxygen Concentrators

It's tragic that most medical insurance providers won't meet their patients' needs and help them get the medical equipment that's right for them and their lifestyle. That's why we've made it our mission to offer portable oxygen concentrators at the lowest possible price, so you can afford to get the oxygen delivery system that's best for you.
The way we do it is by buying large quantities of wholesale portable oxygen concentrators in bulk so we can get the best prices on the equipment and keep our own costs low. That way, we can pass the discount on to you and offer portable oxygen concentrators at extremely low prices that you won't find anywhere else.
Our portable concentrators are so inexpensive that the manufacturers we buy from won't allow us to advertise our best prices on our website. You'll need to download our portable oxygen concentrator price list to see our lowest prices.
At LPT Medical we offer much more than just the lowest-priced portable concentrators around. We also offer monthly financing to make our equipment even more affordable and have a selection of like-new, used portable oxygen concentrators at an even further discounted price.
Solution #2: We Offer the Best Quality Second-Hand Portable Oxygen Concentrators
Even if you can't afford the cost of brand new equipment, you can get an even greater discount on one of our second-hand portable oxygen concentrators. We offer a good selection of lightly-used and refurbished portable concentrators that are thoroughly tested and reconditioned, so they're basically like new!
Our inventory of like-new portable oxygen concentrators is always changing, so make sure to check back with us often to see what we have in stock. And know that all of our machines are thoroughly inspected tuned up before going up for sale, so you always know you're getting the best quality.
Solution #3: We Offer Low Monthly Payments to Help You Finance Your Portable Oxygen Concentrator

We understand that many people don't have the money to pay for such an expensive piece of medical equipment out of pocket right away. That's why we offer monthly financing options to help you manage the cost and get the portable oxygen concentrator you want.
With our monthly financing program, you can afford the equipment you need now and pay back the cost over time in small monthly installments. That way, you can start benefiting from the comfort of a new portable oxygen concentrator right away.
The best part about our low monthly payments is that they allow you to get the exact brand and model of portable oxygen concentrator that you need without having to drain your savings or go through the insurance run-around. And once you've made your last payment, the oxygen concentrator completely belongs to you!
Solution #4: We Can Assist You in Getting Your POC Covered by Medicare
It's been a long time coming, but we are finally able to offer our patients assistance when it comes to covering the expenses of a portable oxygen concentrator through Medicare. We are one of the only online oxygen concentrator companies to be able to offer this service and we are delighted because it means we are able to get these units into the hands of more people who need them.
Typically, when you buy a portable oxygen concentrator, you're given a reimbursement code. You can then use this code to file a claim with Medicare or your private insurance company. The problem with this is that you are given virtually no assistance or instruction on how to actually file and win a claim with your insurance company.
With our new program, however, our respiratory specialists will work one on one with you and Medicare to help you get the reimbursement that you deserve! At the end of the day, this means you have one less thing to worry about. Medicare jargon can be confusing, but when you work with our team, you won't need to waste any time learning about it only to be disappointed that Medicare doesn't give you the answer you expected or wanted. Simply hand the work off to us and we'll gladly take care of it!
Consider Your Options for a New Portable Oxygen Concentrator Today!

There are many ways you can benefit from using a portable oxygen concentrator instead of a multitude of heavy, cumbersome tanks. Using a portable oxygen concentrator can improve your mobility, allow you to travel, and can make a huge difference in your comfort and quality of life.
That's why it's important to us to help more people like you get the best portable oxygen concentrators at a reasonable, affordable cost. Because of our low prices and financing options, more people than ever before are able to afford and experience the benefits of using a portable oxygen concentrator.
Contact us today or call 1-800-946-1201 to get more information on our products and financing options. We can help you find the best option and experience the life-changing freedom of using a portable oxygen concentrator.


 So we can find the best portable oxygen concentrator for your needs!
So we can find the best portable oxygen concentrator for your needs!













