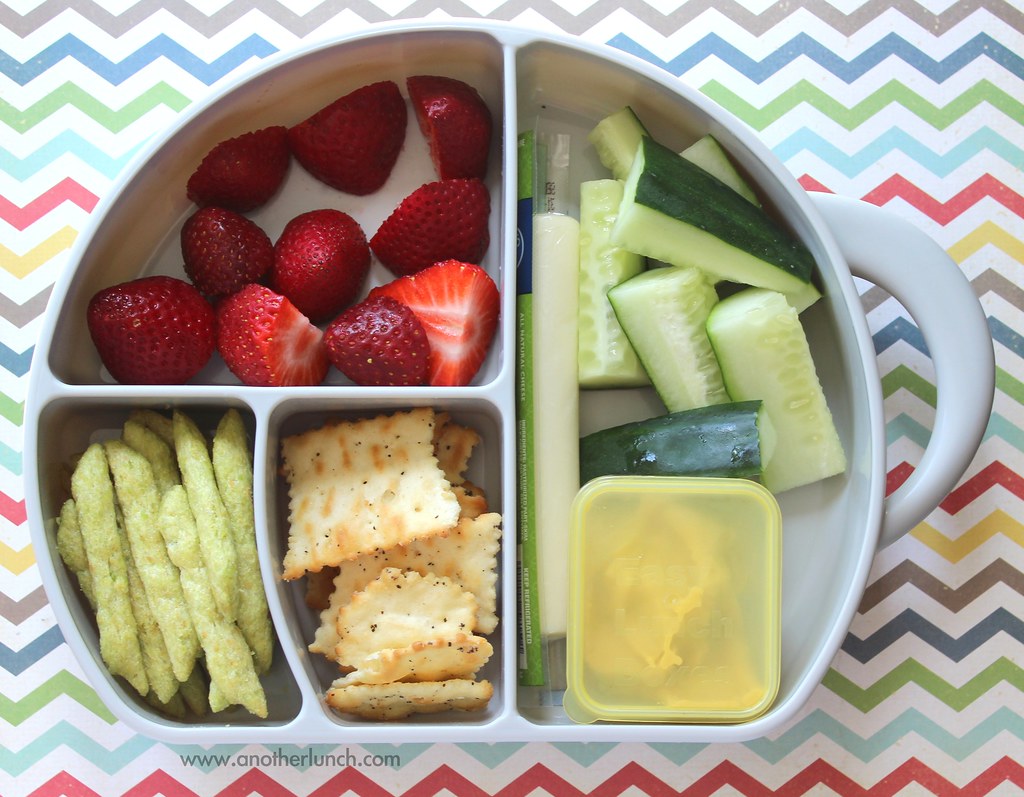
 |
| Image Courtesy of Melissa on Flickr |
If you or someone you love has COPD, you might be concerned about diet and nutrition. What kinds of foods should you eat to stay healthy, and what should you avoid?
Eating right and sticking to a healthy diet is one of the best things anyone can do to feel good and keep their body healthy, with or without a chronic disease. In reality, however, eating well is difficult to do on a daily basis.
Even though just about everybody knows how important good nutrition is, many people still don't practice a healthy diet. This is sometimes due to a lack of time and motivation, but can also be a result of simply not knowing what kinds of foods are actually good for you and not.
If you have COPD, it's especially important to understand what a proper diet looks like and how to incorporate healthy foods into your everyday life. That's why, in this post, we're going to tell you about a wide variety of healthy foods you can eat to help you feel better and stay healthy with COPD.
Why a Nutritious Diet is Important for COPD
 |
| Image courtesy of FoodFacts on Flickr |
Living with a disease like COPD can make everyday tasks like eating more complicated. Many people with COPD even have to eat special, high-calorie diets to make up for the strain that the disease puts on their bodies.
COPD forces you to pay extra attention to many aspects of your health, including diet and nutrition. If you don't get all the vitamins and nutrients you need, you can experience increased COPD symptoms and accelerate how quickly your disease gets worse.
When you are struggling to manage a chronic disease like COPD, it's important to make every meal count by choosing foods that are wholesome and nutrient-dense. Eating healthy meals full of lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and healthy fats is key for maintaining a healthy weight and keeping your body strong.
You should also know that that what's not in certain foods is sometimes just as important as what is. Unhealthy foods with empty calories don't do you any good, and in the worst cases can contribute to weight gain, heart disease, and other health problems. That's why you should avoid processed foods and anything packed with sugar, simple carbs, and unhealthy fats.
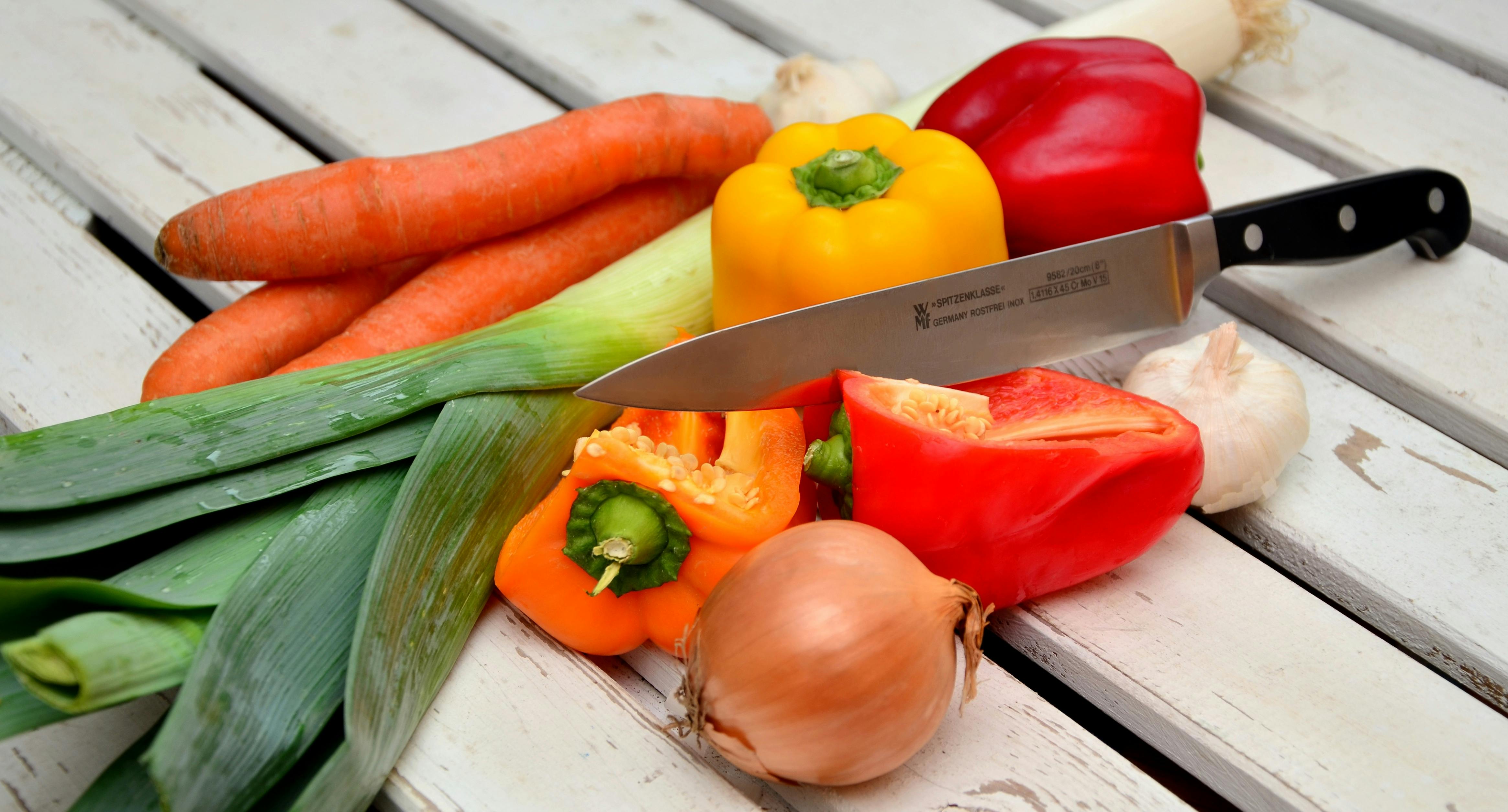
Even among foods considered “healthy,” some are better than others at supplying your body with the nutrients it needs. There are many fruits, veggies, meats, and dairy products that are particularly rich in important vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, and other things your body needs to stay healthy with COPD.
It's much easier to make healthy decisions when you know what's good for you and have a lot of options to choose from. That's why we're providing you with the following list of 21 healthy foods for COPD to help you get started.
While you don't have to get every single item on this list, you should still eat a varied diet of healthy foods from different fruit, vegetable, dairy, and grain categories. This list will introduce you to the nutrient content and health benefits of a wide variety of foods so you can better understand how to meet all your nutritional needs.
How the Food You Eat Affects Your COPD

Before we get to the list, there are a few special factors you should take into consideration when planning a healthy diet for COPD. Certain foods, large meals, and weight gain can actually make your symptoms worse, so you have to pay extra special attention to what you eat.
{{cta('fa8abc2a-1e88-4fa3-82fd-1cb5b9ed43b2','justifycenter')}}
Inflammation
First of all, people with COPD should avoid eating foods that are known to cause inflammation. That's because inflammation puts strain on your body and takes energy away from your lungs, where it's most needed.
Foods that can cause inflammation include high-sugar foods like soda and sweets as well as processed meats like sausage. Besides being inflammatory, these foods are hard on your body and don't contain the nutrients your body needs to effectively manage your COPD.
Instead, you should eat healthy produce like leafy greens and fruits and veggies with lots of vitamin C and vitamin A. This helps your body get the nutrients it needs to prevent and manage inflammation and can improve how well your lungs function.
Manage Weight Gain and Weight Loss

Maintaining a healthy weight is also a top health priority if you have COPD. Both being underweight or being overweight can hurt your lung function and make it more difficult to breathe.
If you are underweight, you're likely to have worsened symptoms like weakness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Weight loss and malnutrition can also weaken your immune system, break down your muscles, and increase your chances for infection, exacerbations, and death.
Excess weight is particularly dangerous for people with COPD, because it can quickly start a downward spiral of physical decline. Being overweight makes it more difficult to stay active, puts extra weight and strain on your chest that makes it difficult to breathe, and also increases the amount of oxygen your body needs to function.
Pay Attention to Antioxidants

Research shows that people who have COPD experienced increased oxidative stress in their lungs and elsewhere in their bodies. This means that they have an excess of inflammatory compounds, called oxidants, that can cause irritation, tissue damage, and other complications.
Every person's body produces antioxidants, which are molecules that neutralize oxidants and prevent them from doing harm. Most healthy people are able to produce enough anti-oxidants to keep the oxidants in check, but people with COPD often don't.
Research shows that people with COPD have an excess amount of oxidants that throws off their body's delicate oxidant/antioxidant balance. When this happens and the balance tips in favor of oxidants, it causes oxidative stress.
That's why some doctors recommend that people with COPD counteract their elevated oxidant levels by increasing their dietary antioxidant intake. There are many fruits, vegetables, and other foods that are rich in antioxidants, and it's thought that eating more of these foods can help your body restore a proper oxidant/antioxidant balance.
Some of the most common antioxidants include vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, selenium, and manganese, which are abundant in a variety of fruits and vegetables. However, research on antioxidants in foods is still ongoing, and researchers don't yet know if eating antioxidant-rich foods is a reliable way to combat oxidative stress.
Eat Fewer Carbohydrates

If you have COPD, you should avoid simple carbohydrates at all costs. Not only are simple carbs empty calories, but having too many carbohydrates in your diet can actually make your COPD symptoms worse.
To understand how carbohydrates affect COPD, you have to first understand how your lungs process carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a waste product that is made from all kinds of metabolic processes in your body, including when you digest food.
When foods are broken down, the carbon waste products go into your blood and are carried to your lungs. When you breathe, the carbon waste is expelled from your body via carbon dioxide in your breath when you exhale.
Carbohydrates, in particular, tend to produce a lot of carbon waste compared to other nutrients, like fat and protein. This means that carbs increase the burden on your lungs to expel the carbon dioxide waste. which can lead to increased COPD symptoms like breathlessness and wheezing.
This is why most doctors recommend that people with COPD eat a diet that's high in fats and low in carbohydrates. This reduces strain on the lungs, reduce COPD symptoms, and make it easier to breathe and exercise.
Eat Small Meals

Doctors often recommend that people with COPD forego traditional mealtimes and instead eat 4-5 smaller meals spaced throughout the day. That's because, when you eat larger meals, it can put pressure on your lungs and diaphragm and make it more difficult to breathe.
Smaller meals are easier to digest and are less likely to cause bloating, indigestion, and breathing discomfort. It also helps you control your portion sizes and eat a wide variety of healthy foods every day.
Eat Nutritious, High-Calorie Foods

Many people with COPD have to eat extra calories every day to make up for the extra energy that their respiratory muscles use to breathe. If your doctor puts you on a high-calorie diet, it's important to fill in those extra calories with healthy, nutrient-packed foods.
Many of the highest-calorie foods are also the least nutritious; think of ice cream, soda, potato chips, and other processed snacks, for example. Instead of eating junk foods with empty calories, choose nutrient-dense, high-calorie foods like nuts and dairy. That way you can get enough calories and maintain a healthy weight while also limiting the amount of salt, sugar, and simple carbs in your diet.
A Final Consideration: Talk to Your Doctor
Depending on your unique physiology and the severity of your disease, you might have special dietary needs and restrictions. That's why, as one final consideration before we get to the list of healthy foods you should eat for COPD, we want to emphasize the importance of talking to you doctor about diet and nutrition.
Your regular doctor or a dietitian can often give you valuable, individualized advice that you can't get anywhere else. They can also help you put together a personalized nutrition plan to help set you on the right track.
As long as you don't have special dietary restrictions, you can use all the foods on this list to make a wide variety of healthy meals. So, without further delay, here's 21 healthy foods you can eat as part of a healthy diet for COPD.
21 Healthy Foods You Can Eat to Stay Healthy with COPD

Foods Packed with Healthy Carbohydrates
Research shows that, when you have COPD, eating too many carbohydrates increases the strain on your respiratory system and makes it more difficult to breathe. While a certain amount of carbohydrates are necessary for a balanced diet, you should eat them in moderation and choose whole foods packed with complex carbohydrates like whole grains and wheat pastas.
Researchers recommend that people with COPD get about 25% of their calories from carbohydrates.
Ancient Grains (Including Quinoa, Barley, and Buckwheat)

Quinoa, buckwheat, and barley, are among a group of whole grains often known as “ancient grains.” Ancient grains are different from modern grains in the sense that they have changed very little over the past several hundreds of years.
Ancient whole-grains are especially rich in fiber, protein, and vitamins, and also tend to be more calorie-dense than modern whole grains. For example, one cup of spelt has about 7.5 grams of fiber and 10.7 grams of protein, while a cup of brown rice only has about 3.5 grams of fiber and 5 grams of protein.
Quinoa, black rice, and other ancient grains are easy to prepare and great for digestion. They also contain high amounts of magnesium, which is extremely important for lung function and may even help prevent COPD exacerbations.
What's more, quinoa and buckwheat are naturally gluten-free, which makes them a great option for people with Celiac disease or other gluten intolerances. If you're looking to add healthy carbohydrates to your diet, the ancient grains are a great place to start.
Here are some examples of healthy ancient grains:
- Quinoa
- Millet
- Black BarleyBlack Rice
- Spelt
- Teff
Whole-Grain Breads and Pastas

Whole grains like wheat breads and wheat pastas are an important part of any healthy diet, but they can be particularly important for people with COPD. A diet rich in whole grain foods can reduce inflammation, improve digestion, help you maintain a healthy weight, and even reduce your risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Breads, rolls, crackers, tortillas, and pastas can all be healthy sources of carbohydrates when eaten in moderation. However, you should always opt for nutritious, whole-grain versions of these foods instead of the less-healthy, processed white grains.
White breads and pastas have been stripped of much of their nutritional value and are full of simple carbohydrates that can raise your blood sugar and leave you feeling less satisfied after meals. Whole-grain carbohydrates, on the other hand, fill you up and provide energy for much longer because they take more time to digest.
Oats

Photo by: Favorece
Like other whole grains, oats are a great source of healthy carbohydrates and fiber for people with COPD. A diet that includes regular helpings of oats can reduce your risk for cardiovascular disease, cancer, and type 2 diabetes.
One of the best things about oats is their high amounts of soluble fiber, which is known to lower cholesterol and prevent heart disease. It also contains a lot of short-chain fatty acids, which improve digestion and are known to have potent anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties.
Foods Packed with Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are perhaps the most important nutrients you should seek out if you have COPD. Most doctors recommend eating a low-carb, high-fat diet because it can improve COPD symptoms and reduce the amount of strain that eating puts on your respiratory system.
A high-fat diet allows your body to get the extra sustenance it needs to breathe without upsetting your nutrient balance. However, it's till important to watch your fat intake so it doesn't become excessive, especially if you are at risk for heart disease.
Most doctors recommend that people with COPD get about 55% of their calories from fat.
Vegetable Oils

While it's important to eat a lot of healthy fats when you have COPD, it's just as important to choose the right kinds. You should try to use unsaturated fats, like vegetable oils, which are considered much healthier than saturated animal fats like butter and lard.
Plant-based fats like olive oil and vegetable oil have been associated with a variety of health benefits, including lowered cholesterol and a reduced risk for heart disease and type 2 diabetes. When cooking on the stove or adding any fats to your meals, try to use plant-based, unsaturated fats as much as possible.
But how do you tell saturated and unsaturated fats apart? A good rule of thumb is that unsaturated fats (like vegetable oils) are liquid at room temperature, while saturated fats (like butter) are not.
Olive oil, in particular, tastes great on meats, breads, in marinades, and in dressings. Try mixing olive oil with your favorite vinegar and spices to make a delicious homemade salad dressing that's full of healthy, unsaturated fat.
Here are some examples of healthy vegetable oils:
- Olive Oil
- Canola Oil
- Peanut Oil
- Soybean Oil
- Sunflower Oil
- Safflower Oil
- (Avoid coconut oil and palm oil, because they contain a lot of saturated fat.)
Cold Water Fish
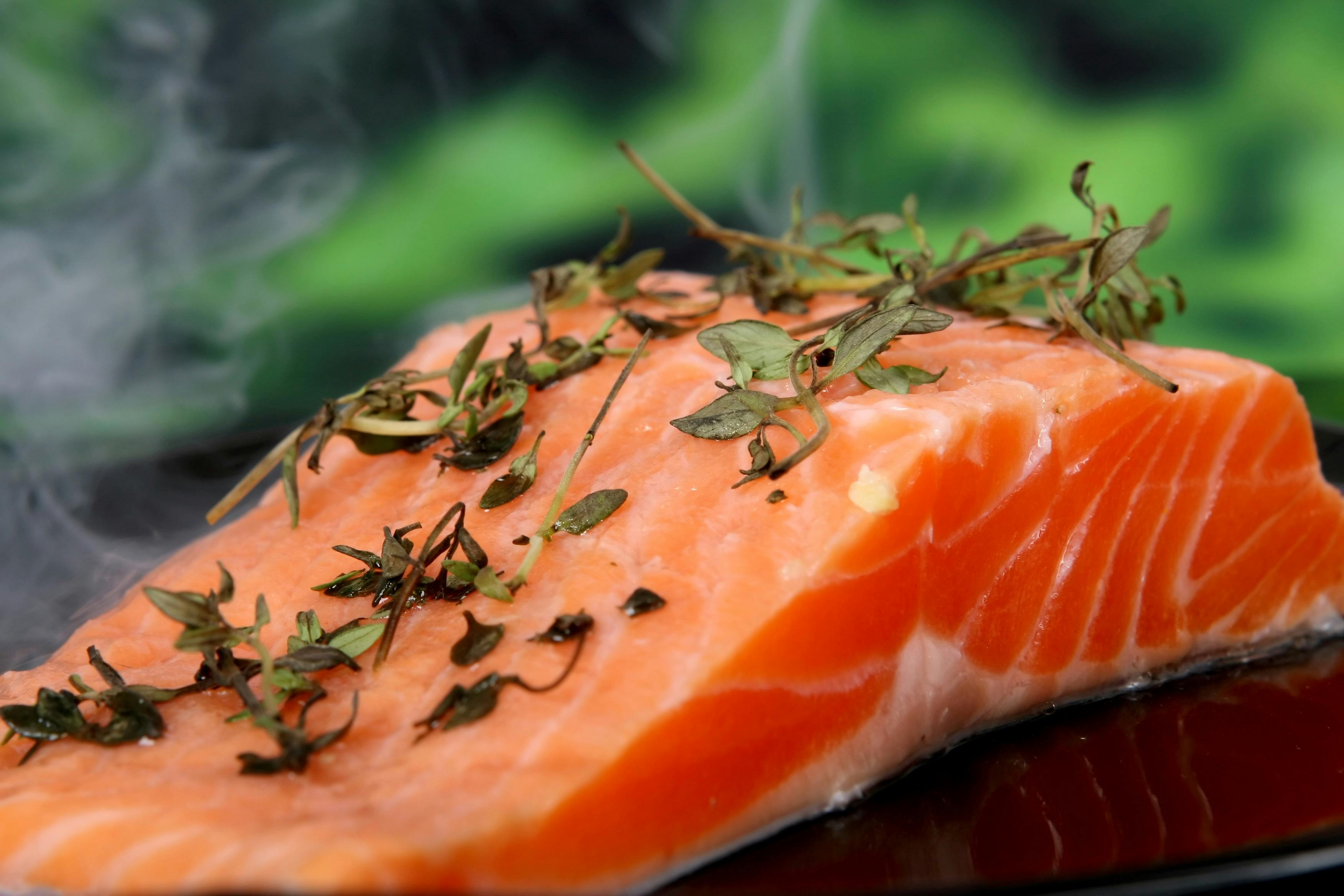

Cold water fish are a fantastic source of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3's are a particularly healthy type of fat which is known to improve lung function, prevent heart disease, and reduce your risk for infection and inflammation. Salmon, tuna, trout, cod, and anchovies are just a few examples of cold water fish that are high in omega-3.
When picking out fresh fish at the store, you should opt for wild-caught varieties, which tend to be cleaner and higher in omega-3's. Farm-raised fish are often fattier, less nutritious, and sometimes grown in dirty environments.
However, one thing you should watch out for when adding extra fish in your diet is eating too much mercury. Fish like tuna, mackerel, and salmon are known for having higher levels of mercury, and it's important to follow US guidelines and only eat high-mercury fish in moderation.
Here are some examples of healthy cold water fish:
- Cod
- Haddock
- Herring
- Atlantic Mackerel
- Mahi Mahi
- Trout
- Salmon
- Pollock
- Whitefish
- Sardines
Nuts

Nuts are high in calories, but they are also chock full of healthy protein and unsaturated fats. Nuts also tend to be high in fiber, vitamin E, and plant sterols, which can reduce blood cholesterol levels.
Nuts are known for containing heart-healthy nutrients that can help protect your arteries and reduce your risk for heart disease. This makes them a great option for people with COPD who are at a higher risk for cardiovascular complications.
Nuts are also a great choice if you are underweight or want to prevent COPD-related weight and muscle loss. They are nutritious and delicious to eat raw and take little or no preparation, but they still contain enough calories and protein to help you stay strong and maintain a healthy BMI.
Nuts are perfect for satisfying hunger in-between meals and they're exceptionally easy to pack up and take with you for an extra snack when you leave the house. They're also a great addition to meals; try adding some extra nuts to salads, rice, meat dishes, and baked goods for an extra dose of healthy fat and protein.
Here are some examples of healthy nuts:
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Pistachios
- Cashews
- Brazil Nuts
- Pecans
- Macadamia Nuts
- Hazelnuts
Foods Packed with Healthy Protein
Lots of lean, healthy protein is important in any diet, but it should be a special priority for anyone with COPD. People who suffer from the disease often have difficulty getting enough protein, which can cause their bodies to break down their own muscles and become weak.
Doctors recommend choosing lean sources of protein like fish, eggs, and dairy instead of red and processed meats like bacon and ground beef. Most people need about 1.5 grams of protein for every 2.2 pounds of body weight, and doctors recommend that people with COPD get about 20% of their calories from protein.
Beans and Legumes

Beans and legumes are great sources of protein because they are lean, nutritious, and absolutely packed with fiber. They are also a good source of complex carbohydrates and contain a lot of zinc, which research shows may improve COPD symptoms and increase levels of beneficial antioxidants.
Beans and legumes are also one of the most inexpensive sources of healthy protein, especially if you buy dried beans and cook them yourself. However, canned varieties are also notoriously cheap and they're a great choice if you need to conserve time and energy.
A single ½ cup serving of beans contains about 8 grams of protein, 8 grams of fiber, and at least 300 milligrams of potassium. Beans make a hearty and flavorful addition to just about any meal, and they're especially delicious in rice dishes, soups, and salads.
Here are some examples of healthy legumes:
- Red, green, and brown lentils
- Chickpeas
- Soybeans
- Edamame
- Kidney beans
- Split Peas
Chicken and Other Lean Meats

Chicken is lean, inexpensive, and one of the best healthy sources of protein. Chicken is a great daily staple because it's nutritious, extremely versatile, and relatively easy to prepare.
To keep your chicken lean and healthy, choose white meat instead of dark meat and remove the skin, which is the fattiest part. It's also best to cook your chicken by grilling it or baking it in the oven, that way you can avoid adding extra fats as you have to when preparing it by pan-frying or deep-frying.
Try eating grilled or baked chicken along with rice, pastas, soups, and veggies. There are endless ways to prepare and flavor chicken, so get creative and try different dishes so you never get tired of this great protein source
Supplemental oxygen is a type of medical therapy used to treat chronic lung conditions like cystic fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis, and COPD. The aim of supplemental oxygen is to maintain a patient’s blood oxygen levels which are vital for systemic health. Every organ in the body requires oxygen in order to function properly, so using supplemental oxygen as it’s advised by your doctor can provide you with immense short- and long-term benefits.
Despite how important supplemental oxygen is for respiratory patients, receiving a prescription for oxygen therapy can be a scary experience. You likely have a lot of thoughts and concerns running through your mind and you’re likely overwhelmed by the prospect of being connected to an oxygen delivery device. While these concerns are certainly justified, it’s important to take a step back and begin to clarify your concerns with your doctor. Chances are, as you learn more about oxygen therapy and become more experienced with using it, many of your concerns will begin to disappear.
To help you organize your thoughts, we’re going to be discussing 14 questions you should ask your pulmonologist about supplemental oxygen therapy. Feel free to either print out this article or take notes so that you know exactly what to ask your doctor during your next visit. If you enjoy this article and you’re looking for more information, be sure to read through our post titled “16 Questions You Should Ask Your Doctor About COPD.”
1.) Is Oxygen a Necessity or a Suggestion?
Chances are, you or someone that you know has fallen back on a prescription at some point. Either you never make it to the pharmacy to pick up your medication or you simply stop using the medication for one reason or another. This Harvard Medical report states that many people either forget to use their medication, or they never fill it due to high copayments. So, naturally, you might wonder whether or not your oxygen therapy prescription will follow a similar trend. As a general rule of thumb, you should take what your doctor says seriously, because it’s unlikely that he/she would make you go out of your way or spend extra money on something that isn’t necessary. However, it doesn’t hurt to address these concerns so that your doctor can clarify the rationale behind your oxygen prescription.

2.) What are the Benefits of Oxygen Therapy?
The second thing you should ask your pulmonary doctor about are the benefits you can expect to reap from using supplemental oxygen. The air around us contains about 21% oxygen, but for someone with impaired lung function, this is not always enough for them to sustain their blood oxygen levels. The goal of oxygen therapy is to provide the lungs with a higher concentration of oxygen in order to reduce the load on the lungs. You may experience additional benefits from using supplemental oxygen based on the severity of your disease. Be sure to ask your doctor about this.

3.) What is My Flow Rate?
Your flow rate determines the amount of oxygen that you will be receiving when you put on the nasal cannula. It’s imperative that you know the exact amount of oxygen that you should be receiving because inhaling too much oxygen can lead to a condition called oxygen toxicity. This condition results in dizziness, fatigue, nausea, and eventual lung damage. Conversely, receiving too little oxygen will not provide you with the full benefits of supplemental oxygen.

Oxygen flow is measured using one of two different measurements. Pulse dose oxygen devices are measured in milliliters per minute (ml/min) and continuous flow oxygen devices are measured in liters per minute (LPM). The amount of oxygen that you’re prescribed will be based on the severity of your respiratory impairment, but generally speaking, most people need less than 2 LPM of oxygen.
4.) How Many Hours a Day Should I Use Oxygen?
Knowing how long you should be using oxygen is just as important as knowing your oxygen flow setting. If you’re using oxygen inconsistently, you might see a lot of your respiratory symptoms start to return. Long-term oxygen therapy is usually done for at least several hours a day, and your doctor will work with you to determine the best time to use it. If your doctor prescribes you with 24/7 oxygen, then you should discuss with your doctor about using an oxygen concentrator which doesn’t need to be refilled constantly like oxygen tanks or liquid oxygen tanks.

5.) What Type of Oxygen Device Should I Buy?
You might be surprised to find out how many oxygen devices there are on the market. You’ll have a whole host of options to choose from including traditional oxygen tanks, liquid oxygen tanks, stationary oxygen concentrators, and portable oxygen concentrators. But as someone who’s new to supplemental oxygen, you likely don’t know where to even begin with choosing one of these. Your doctor will likely have some information for you regarding which oxygen devices you should avoid and which ones you should consider.

It’s important to be careful when you’re purchasing an oxygen device. You may encounter companies that try to sell you oxygen without a prescription or that boasts prices that are significantly lower than any other company. However, these are most likely scams. Before making any decisions, be sure to research the company that you’re buying from to make sure that their products are reliable and that they follow all laws and regulations. For more information about how the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates oxygen, please visit this page.
If you need a quick reference the ARYA Airtivo Max is a pulse flow portable oxygen concentrator that only weights 4.2 pounds, and has pulse flow operational setting from 1 through 6. This is a best selling oxygen device. It is very popular among oxygen users that live active lifestyles. The battery powered device are great for travel and everyday activities!
6.) Is it Okay to Adjust My Flow Rate Depending on How I’m Feeling?
If you have a chronic respiratory condition like COPD or pulmonary fibrosis, it’s not uncommon for symptoms to come and go. One day, you might be out of breath or lightheaded and the next you could feel perfectly fine. Because of this, you’re going to want to clarify with your doctor when it’s okay to adjust your oxygen flow and when you should not adjust your oxygen flow. The reason it’s important to ask this question is because your increase in symptoms may be due to something completely unrelated to your blood oxygen levels. In which case, increasing your oxygen flow would not benefit you.
.jpg?width=461&name=CAIRE_FreeStyle_Comfort-Nursery_10%20(1).jpg)
7.) How Can I Track My Blood Oxygen Level?
A pulse oximeter, or pulse ox device, clips onto your finger and measures the saturation of oxygen in your blood (SpO2). They are noninvasive and they work by passing rays of light through your finger to measure the amount of oxygen-carrying hemoglobin. While they aren’t the most accurate method of measuring blood oxygen levels, they are very lightweight and portable meaning you can pack one in your purse or handbag for easy access. If your doctor hasn’t already provided you with one, it’s worth mentioning it so that you have a way of monitoring your oxygen levels. To learn more about blood oxygen levels, read this post.

8.) Is Oxygen Therapy Safe?
Since oxygen is a controlled substance in the United States and requires a prescription, you may be wondering if it’s even safe to use in the first place. The answer to this question is “yes,” however, there are some things you should be aware of. Firstly, as aforementioned, using more oxygen than you’re prescribed will put you at risk of experiencing oxygen toxicity. Secondly, the safety of oxygen therapy depends heavily on the type of oxygen device you’re using.
Traditional oxygen tanks are the most dangerous because they contain compressed oxygen and they’re also heavy and bulky. Portable oxygen concentrators are the least dangerous oxygen device because they are lightweight and do not contain compressed oxygen. Oxygen is an “oxidizer” meaning it increases the flammability of anything it comes into contact with. So, you should never smoke near your oxygen device or use it near an open flame.
9.) Should I Be On Oxygen When I Sleep?
If your doctor prescribes you with 24/7 oxygen, you might be wondering how this will work when you’re sleeping. Your breathing rate and depth fluctuate a lot when you sleep so the amount of oxygen that you’re receiving could change throughout the night. This is why it might be worth it to invest in a portable oxygen concentrator like the Caire FreeStyle Comfort or the Inogen One G5. Unlike oxygen tanks, these devices closely monitor your breathing as you sleep and adjust your intake accordingly.

If you have a sleep disorder like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), you may need to use your PAP device and your oxygen device at the same time while you sleep. PAP therapy is of critical importance for OSA patients because it keeps their airways open as they sleep allowing them to get restful sleep without interruptions. To use your CPAP device with your oxygen device, you need to be using a continuous flow oxygen unit and have a bleed in adapter that connects the tubing together. The Respironics SImplyGo is the perfect portable oxygen concentrator for CPAP compatibility.
10.) How Can I Eliminate Discomfort While on Supplemental Oxygen?
For the most part, oxygen therapy shouldn’t cause any discomfort. However, some people encounter issues with the nasal cannula such as irritation inside the nose due to dryness or some other reason. Humidifiers can actually be attached to your oxygen device to help ease the discomfort and there are a number of other accessories you can purchase that make the process more comfortable. We actually wrote a guide discussing some of the issues oxygen patients face and how to solve them. Check it out here.

11.) Can I Exercise on Oxygen?
Consistent moderate exercise is crucial for pulmonary wellness. Not only does exercise improve the strength of your lungs but it also increases the efficiency that your heart pumps oxygen throughout your body. So, just because you’ve started oxygen therapy does not mean that you should stop exercising. Check out this post which has some tips for exercising with an oxygen device and be sure to ask your doctor for advice as well.

12.) What Do I Need to Know to Travel With Oxygen?
Traveling around the world with COPD is much easier than ever before thanks to portable oxygen concentrators. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), the organization that oversees all commercial flights in the United States has approved most POCs for in-flight use. However, to make sure you have everything you need, you should contact your airline at least 48 hours before your flight. Most airlines require that you have at least one and a half times as much battery life as the duration of the flight. This will make up for any delays that may occur before and after you land.

13.) How Do I Maintain My Oxygen Device?
With the advent of the novel coronavirus, cleaning has taken on a whole new meaning. No matter what type of oxygen device you decide to use, you should take the time to clean it regularly. What’s more, nasal cannulae and oxygen tubing should be replaced every two weeks to ensure it’s clean and ready for use. If you purchase a portable oxygen concentrator you should remove the particle filters each week and wash them off. This will ensure that the air you’re inhaling through the cannula is clean and free of dust and dirt.

14.) Will I Need to Get Retested For Supplemental Oxygen?
Doctors typically use arterial blood gas analysis, pulse oximetry, and various lung tests to determine your need for supplemental oxygen. However, you may need to take on-going tests to help your doctor determine whether or not you still need oxygen in the future. Ask your doctor what kind of tests you will need to take and how often you should come in for a checkup once you are using your oxygen device. Some patients find it helpful to get a certificate of medical necessity which can help you file insurance claims and apply for benefits.


Breathlessness on its own can make walking, bending, kneeling, and other physical tasks exhausting and uncomfortable. And then when you add other COPD symptoms into the mix, like coughing, wheezing, muscle weakness, and fatigue, daily responsibilities like cooking can sometimes seem like too much to handle.
Because of this, conserving energy is often a necessity for COPD patients, especially when they experience flare-ups, exacerbations, or begin to lose their physical mobility as the disease progresses. That's when it's time to start looking into effort- and time-saving tools and techniques and ways to simplify and streamline daily tasks.
Nowhere is this more important than when it comes to food and cooking. Diet is a vitally important part of staying healthy with COPD, but it's also easy to neglect when you're not feeling well. Continuing to purchase and prepare healthy, whole meals can get extremely difficult when you're restricted by limited strength and energy every day.
That's why, in this article, we're going to help you find ways to continue shopping, cooking, and preparing healthy meals in spite of the difficulties that come along with having COPD. We'll show you how planning your meals and using a variety of practical tools and techniques can significantly reduce the amount of time and effort you have to spend shopping and preparing home-made food.
We'll teach you some practical shortcuts for meal planning and preparation, show you how to save energy cooking and cleaning, and introduce you to food-related products and services designed to help people with limited mobility. So without further ado, continue reading to learn about 27 useful tools and techniques you can use to simplify grocery shopping, meal planning, and cooking with COPD.
Tools & Techniques for Easy Meal Planning

Planning ahead is the cornerstone of efficient cooking. Without a weekly meal plan, shopping and preparing meals is much more stressful and you're more likely to just give up and opt for processed or fast foods.
On the other hand, putting a little extra effort into scheduling your meals helps to streamline the entire shopping, food preparation, and cooking processes. This section will give you a variety of practical tips to help you successfully build the habit of planning your meals ahead for every week.
Writing Your Meal Plan
It might seem like a pain, but taking the time once a week to sit and write down every meal you're going to eat is guaranteed to save you time and effort in the long run. It streamlines shopping, simplifies cooking, and helps you fit healthy, homemade meals into your busy week.
When planning your meals, make sure you consider how much time you have each day and do your best to be realistic. Always have a couple of quick-fix or pre-made meals in mind as a contingency plan for when your schedule changes or you just don't have enough time to cook.
Once you get into the habit of meal planning, you'll start to notice a myriad of benefits. It will remove the stress of wondering “what can I make for dinner?” every evening, and saves time when it's time to make your shopping list.
If you follow a meal plan, you won't find yourself without the ingredients you need to make dinner, because you'll know exactly what groceries you need and you can shop for all your meals for the week ahead of time. By making things as easy for yourself as possible, it will also be easier to stay committed to making home-cooked meals, and easier to resist unhealthy, lazy options like fast food.
Here are some additional tips for weekly meal planning:
-
Record your meals in a weekly schedule or calendar so you can easily remember and keep track of your meal plan
-
Plan the most difficult or time-consuming meals for days when you have fewer activities and are less likely to breathless or worn out.
-
Avoid having to cook every single day by planning for leftovers or heating up make-ahead meals (prepared ahead of time).
-
Plan no-cook meals like sandwiches and salads for busy days or use them as a fall-back for when your COPD symptoms act up.
-
Plan slow cooker meals for days when you don't have time for a lot of preparation or cooking. Simply throw the ingredients in the pot in the morning, and you'll have a hot, delicious meal waiting for you at the end of the day.
- Make your shopping list while you're planning your meals for the week. That way, you can add all the ingredients you need for your meals to your shopping list and take care of two birds with one stone.
Keep Track of Recipes

It's hard to plan your meals if you don't know what to make. That's why building up a collection of your favorite recipes can really help you out.
If you often have trouble thinking of what to make or you're getting bored with your usual meals, it might be time to go shopping for a new cookbook or two. Look for cookbooks with practical recipes that appeal to your tastes and aren't too complex for you to make. Mark your favorite recipes with post-it notes or copy them into a separate notebook so you can easily find and flip through the best recipes.
It's also a good idea to spend some time searching online for recipes and recipe websites that you like. Look for themed recipe blogs that focus on types of food you enjoy and bookmark any sites or single recipes that you want to keep.
You can also use a note-taking and bookmark-organizing application like Evernote to save and keep track of any recipes you find on the web. That way, you can sort your recipes by category and easily track down any recipe you've saved.
Plan Around Themes

Assigning a theme or main ingredient to different days of the week can take some of the pressure and hassle out of meal planning. It could be any theme you want; you could try taco Tuesdays, fish Fridays, soup Sundays, or casserole Mondays. Whatever you choose, it will narrow down your options and make it easier to pick out meals for the week.
But just because a day is dedicated to a particular type of meal doesn't mean you have to eat the same thing every time. Instead of preparing the same boring meal week after week, use your themed days as an excuse to try out new recipes or variations. For taco tuesdays, for example, you could try a different type of taco every week (e.g. beef tacos, fried fish tacos, veggie tacos, chicken tacos, etc.).
Tools & Techniques to Make Shopping Easier
The long, winding path through the grocery store can be exhausting if you have COPD. Luckily, there are plenty of ways to reduce the amount of time you have to spend shopping for food and supplies.
Whether you suffer from limited mobility or simply need to conserve energy when you're feeling breathless and fatigued, simplifying and streamlining your grocery trips can make a huge difference in your life. Take a look at some of the following tips and techniques for getting the groceries you need with less time, effort, and hassle.
Plan Your Route

If long grocery shopping trips leave you exhausted and breathless, then you should try to keep them as short and efficient as possible. The best way to do this is to have a complete list of everything you need before you go, organized in the order you will encounter the items at the grocery store.
As long as you know the store's general layout, planning your route ahead of time shouldn't be difficult to do. Simply do your best as you write your list to arrange the items into categories (e.g. produce, dairy, and frozen) and put them in roughly the same order as they occur in the store.
This way, you can save energy by taking the shortest path possible through the aisles while still getting everything you need. It also greatly reduces your likelihood of having to backtrack and walk all the way across the store for items you skipped over or forgot.
Shop Once

Almost nothing is more frustrating than arriving home from a grocery trip with more than you need and realizing you forgot the items that you went there for. Then, you either have to make do without, or muster up the energy to make another journey out to the store.
That's why you should never set foot in a grocery store without having a plan. Taking some time to sit down and make a list is absolutely essential for making your shopping trips efficient and worthwhile.
First, take a couple minutes to write down all the meals you have planned for the week and the ingredients you'll need to make them. Then, take a look in your fridge, freezer, and pantry to see what ingredients you have and what ingredients you'll need to get.
You should also make it a habit to check your cabinets for how much of any important food staples, like flour, herbs, rice, and canned goods that you have left. If you're running low on anything, it's in your best interest to buy more before you run out so you don't find yourself having to make a last-minute trip to the store on a later date.
Take Advantage of Local Grocery Store Pickup
 |
| Photo by Joe Goldberg |
Did you know that many grocery stores have a service where they'll pick out your groceries for you, saving you the walk through the store? It's a great way to save energy if all of the walking, lifting, and stooping that grocery shopping requires makes you feel too exhausted and breathless to shop.
Depending on the store, you can either give them a list of the items you need or directly order them online. Then, all you have to do is drive up to the store, and employees will load up all your bags in your car for you.
Get Your Groceries Delivered to Your Door

Many grocery stores also offer delivery services you can use to get your groceries brought right to your house for a fee. This allows you to get all of your shopping done without ever having to leave your home.
There are also many online stores you can use to order groceries for delivery straight to your door. Amazon Prime Pantry, for instance, has a massive selection of groceries and cooking items to choose from and you can get most of them delivered to you in just two days if you pay the annual membership fee for Amazon Prime.
Subscribe to a Local CSA

Being part of a community Supported Agriculture (CSA) program is a great way to support local agriculture and get fresh, nutritious produce during the summer and fall.
It works like this: You pay an annual membership fee that is used to support a local farm. Then, during the growing season, you will receive regular boxes of fresh fruits and vegetables grown on that farm—your “share” of the harvest in return for your investment.
Most of the time, you can pick up your box weekly at one of a few pickup centers in your city. Most CSA's will get you a box of fresh produce every week during the summer and fall, but it depends on how your local CSA works and what kind of membership you pay for.
CSA's are a great way to work more fruits and veggies into your diet without having to pick them out yourself. All you have to do is pick up your box of produce, and you'll have most if not all of your fresh fruits and veggies that you need for the week.
Visit Local Harvest's website to see if there's a CSA program that delivers to your area.
Stock Extras

Many non-perishable foods can keep for months, or even years unopened. Use this to your advantage and stock your home with extras of all the non-perishable items you use on a regular basis.
That way, you don't have to worry about running out of ingredients as quickly and can make fewer trips to the store. It can also save you a great deal of money if you take advantage of sales and special offers or buy things in bulk.
Here are some examples of common non-perishable food items that you can stock for months or years before you use them:
- Sugar
- Flour
- Dry beans
- Rice
- Pasta
- Baking powder and baking soda
- Canned goods
Tools & Techniques to Make Cooking Easier
Simplify Your Cooking Prep Process
Oftentimes, gathering and preparing ingredients is the most difficult part of cooking. Chopping veggies, measuring ingredients, and mincing garlic not only takes time, but saps your valuable strength and energy as well.
Here are some tips to help you reduce the amount of time and effort you put toward preparing ingredients for meals.
Rearrange Your Cooking Space

Many cooking inefficiencies stem from a messy or poorly organized kitchen. If you take some time to tidy up your cooking space and arrange your kitchen supplies for maximum utility, you can noticeably reduce the amount of hassle and time it takes to cook.
For example, put items and ingredients you use often front and center in your cabinets and make sure everything is within easy reach. Have a stool handy to help you reach higher shelves and use a grabber tool to avoid bending down for items in lower cabinets and drawers.
Prepare Ingredients Ahead of Time

Instead of doing all your prepping and cooking at once, which can be exhausting, split them up and do them at different times. For example, you could prepare the ingredients for your dinner in the mornings and then cook in the evening, or pre-chop lots of fruits and veggies on the weekend, when you have some extra time and energy.
It can also help to make large batches of meal staples like rice, beans, pasta, or potatoes ahead of time to use throughout the week. If you store them in air-tight jars in the fridge, most foods will keep for at least 3-4 days after you prepare them.
Find Recipes with Fewer Ingredients
 |
| Photo by Tim Sackton |
Have you ever looked up a recipe online, only to find two recipes for the same dish that have vastly different ingredients? That's because there's more than one way to cook just about everything, and some ways are much quicker and easier than others.
That's why you should look specifically for simpler recipes with fewer ingredients if you want to save energy preparing your meals. Fewer ingredients not only means less dicing, mincing, and measuring, but also means fewer trips to the store for fringe ingredients that you don't keep on hand.
There are several popular three-, four-, and five-ingredient cookbooks out in bookstores and online that are full of tasty recipes that are simple to make. There are also websites and food blogs dedicated to simple, easy cooking that are full of recipes that only use a few main ingredients.
Here are some great recipe websites you could try:
- Stone Soup: A blog full of 5-ingredient recipes and simple weeknight dinner inspirations.
- Six Sister's Stuff: A list of 50 easy recipes with six ingredients or less.
- Good Food from the BBC: A list of 40 quick recipes with five ingredients or less.
Buy Pre-Prepared Produce
Most grocery stores have coolers full of pre-washed, pre-chopped, and pre-peeled fruits and veggies in their produce section. While they are a little more pricey than their un-processed counterparts, buying pre-prepped produce can save you several steps and a significant amount of time when you cook.
Drink Green Smoothies

Green smoothies are a great way to get more healthy fruits and veggies in your diet without having to cook. The only prep work you have to do is washing whatever healthy produce you have on hand and tossing it into a blender.
Smoothies are also a great way to use up extra fruit and veggies that are close to going bad. You can make them anytime you're in a pinch for time or make them a regular part of your everyday diet.
You can make fruit or green smoothies with just about whatever you have on hand, depending on your tastes and nutritional needs. Here is an article with 25 easy green smoothie recipes to help you get started.
No-Cook Meals

There will be days when you're just too tired, too breathless, or too lazy to slave over the stove. Luckily, there are plenty of simple, healthy meals you can whip up that don't require any cooking at all.
No-cook meals are often easier to prepare than hot foods and almost always take less time. They are also great for hot, summer days when you don't want to heat up your house by using the stove.
Here are some ideas for no-cook meals and snacks you can try making at home:
- Green Salads: Use whatever veggies and salad greens you have on hand with a light dressing for a delicious meal or side dish. Try adding fruit, nuts, hard-boiled egg, or meats like salmon and chicken for a heartier, more flavorful meal.
- Chickpea Salads: You can make a delicious Mediterranean salad with nothing but canned chickpeas, veggies, and hummus dressing. Add some pre-cooked quinoa to make it even better.
- Sandwiches
- Lettuce wraps
- Tortilla wraps
- Veggie nachos
- Fruit salads
You can also find a variety of no-cook, cold meal recipes online, like on this list from Southern Living.
Single-Pan and Single-Pot Meals
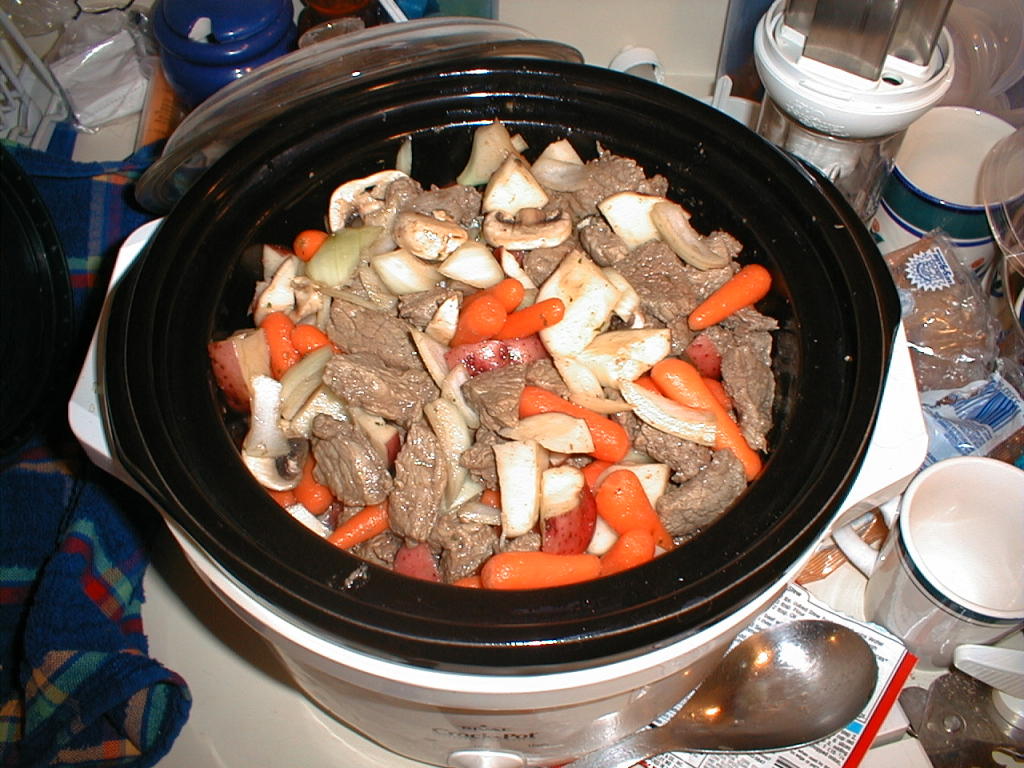

Cooking everything in one big pot or pan can save you a lot of time and energy. It means fewer steps, fewer dishes, and a much simpler cooking process.
Single-pan and single-pot meals can include skillet dinners, casseroles, dutch oven dinners, and slow cooker meals. You can find tons of recipes for one-pan meals online, or easily whip up an improvised meal on your own.
Just about any combination of meat, veggies, and potatoes in a skillet can work to make a delicious, well-balanced meal. Another easy option is to stir-fry whatever vegetables you have on hand and serve them over rice, quinoa, or another healthy grain.
Choose Simple & Easy Foods

If you want to reduce the amount of preparation you have to do to for meals, get the simplest version of the ingredients you can. For example, use frozen or canned carrots instead of peeling and chopping them yourself, or get pre-washed, bagged lettuce instead of a whole head.
Also, consider how difficult a fruit or vegetable will be to prepare before you buy it. For instance, pomegranates, pineapples, and melons take a decent amount of time and effort to prepare for eating. On the other hand, bananas, apples, and berries are require min

Maintaining a healthy amount muscle mass is a constant struggle for many COPD patients, especially those in the later stages of the disease. COPD not only causes weight loss and loss of muscle mass, but it makes it more difficult to build muscle as well.
This is due in part to the nature of the disease, and partially due to COPD symptoms that make it difficult to exercise and build strength. Many people with COPD also get caught in negative habits, like avoiding exercise and meals, or suffer from psychological conditions like anxiety or depression.
All of these things lead to weight loss and muscle wasting, and eventually an overall physical decline. It's not something to take lightly; COPD patients with very low body weight and muscle mass tend to have highest mortality rates and are prone to a variety of complications.
But even though COPD makes it more difficult to build and maintain muscle, it is definitely possible to do. All you need is the right diet, eating habits, and exercise routine to keep your body strong and maintain a healthy BMI.
In this article we're going to tell you everything you need to know about building muscle mass and COPD. We'll explain how the disease affects your muscles, how muscle mass affects your health, and show you a variety of different techniques you can use to better gain muscle and prevent weight loss with COPD.
What Causes Weight and Muscle Loss in People with COPD?

As many as forty to seventy percent of people with COPD experience weight loss and muscle wasting, especially in the later stages of the disease.
There are a variety of reasons why this happens, but lack of exercise and eating too little are the main causes. People who suffer from COPD also have difficulty maintaining their muscle mass because of inflammation and the fact that their damaged lungs need extra calories and nutrients.
Here's a more detailed look at the four main causes of muscle wasting and weight loss in people with COPD:
Too Little Exercise

Most people with COPD have at least some difficulty exercising as a result of respiratory symptoms like shortness of breath. This causes many people with the disease to neglect their exercise needs, which makes the problem even worse.
It's extremely important to get enough physical activity as early on as possible if you have COPD. Those who get diagnosed at early stages of the disease are at an advantage for this reason.
If you stay sedentary for too long, your muscles will get weaker, your respiratory symptoms will worsen, and it will become more and more difficult to tolerate exercise and even mild physical activity. That's why easier to prevent muscle loss than it is to gain it back once it's already gone.
If you have COPD, sticking with you doctor-prescribed exercise routine and being active is the only way to prevent physical decline. There are only two choices when it comes to your muscles: use them or lose them.
Too Little Food
Many people with COPD experience worsened symptoms when they eat. Some patients feel breathless from the energy and act of eating alone, but eating can also cause the stomach to swell and put pressure on the lungs, causing discomfort and shortness of breath.
Because of this, many patients avoid eating or are not able to finish their food at mealtimes. This leads to weight loss and malnutrition, which then causes muscle weakness and wasting. Malnutrition also suppresses your immune system, which significantly increases your chances for infections, exacerbations, and hospitalization.
That's why proper diet and calorie-rich foods are so important for people who have COPD. If you don't eat enough calories and nutrients to sustain your body's needs you will have less energy, you will lose weight, and your body will begin breaking down its own muscles out of necessity.
Depression

It takes a lot of energy and mental strength to cope with getting diagnosed with COPD. It's normal to feel a great deal of anxiety, especially at first, but for some people it can lead to serious depression.
Depression makes it easy to give up on the habits and activities that keep you healthy. It can make you feel too exhausted and anxious to get out of bed, let alone keep up with your prescribed exercise, diet, and treatment regimens.
Because of this, many people with COPD who get depressed let themselves become sedentary and malnourished. This leads to a loss of muscle mass as well as weight loss that can lead to even worse depression and COPD symptoms.
Mental health and physical health are closely intertwined, which is why it's very important to seek help if you are struggling. Look out for the symptoms of depression in yourself and loved ones with COPD, and don't hesitate to talk to a mental health professional if you're having trouble coping on your own.
Untreated anxiety and depression can lead to a variety of health problems and it's no way to live your life. It's possible to find hope and happiness in the midst of managing a chronic illness, and your doctor or psychiatrist can help you take the first steps toward feeling better.
Inflammation

Studies show that people with COPD produce more inflammatory compounds than healthy individuals and show signs of inflammation all throughout their bodies. Researchers have found that this chronic inflammation could be part of the reason that COPD patients are especially prone to muscle wasting.
Inflammatory molecules inhibit the body's ability to generate muscle mass, which makes it difficult to build strength and reverse muscle loss. Instead of putting its energy toward rebuilding and maintaining your muscles, your body has to focus its most of its energy on repairing the tissue damage caused by inflammation.
Chronic inflammation also saps your energy and makes you feel fatigued, which makes it even more difficult to exercise and maintain your muscle mass. This makes people with COPD even more prone to muscle loss, weight loss, and adopting a sedentary lifestyle.
Increased Calorie Requirements
Many people with the disease don't realize that COPD makes you burn more calories than healthy adults. Lungs damaged by COPD have to use up to ten times the amount of energy to breathe, which means you have to eat more food to make up for it.
The more your lung function declines, the more energy it takes to breathe, which means that your calorie needs will likely increase as your disease progresses. If you don't eat extra food to make up for the extra calories you burn, you're bound to lose weight and possibly even muscle as your body breaks down its muscle and fat reserves to get the energy it needs.
Since eating can already difficult and exhausting when you have COPD, many patients are unwilling or unable to get the extra calories and nutrients they need from their meals. That's why many doctors recommend calorie-dense foods like milk and nuts; it allows you to get more sustenance from a smaller amount of food, so it's easier to eat enough to meet your body's needs.
The Dangers of Weight Loss & Muscle Loss for People with COPD
Both a certain amount of muscle and a certain amount of fat are necessary to stay healthy and strong, especially if you have COPD. Additionally, both weight and muscle mass are closely related; weight loss usually leads to muscle wasting and muscle wasting can also lead to weight loss.
If you have COPD, it's not just important, but vital to stay at a healthy weight and keep up your muscle mass as much as possible. It's considered to be a very bad sign if you start losing weight or muscle mass quickly, and reversing the loss is the only way to preserve your lung function and health.
Research shows that COPD patients with a BMI under 20 have less energy, worse symptoms, and quicker respiratory decline. A low BMI also puts you at risk for infections, exacerbations, hospitalizations, and other serious complications.

Another consequence of being underweight is malnutrition, which can be devastating for someone with COPD. Being underweight and undernourished depresses your immune system, causes muscle wasting, and leaves you without enough energy to exercise or do normal daily activities.
This starts a downward spiral that leads to even more muscle loss, more difficulty exercising, and worse COPD symptoms. Because of this, low body weight and muscle mass (if not treated and reversed) are considered reliable predictors of a quicker overall decline in physical health.
Rapid, severe weight loss is a sign of a very serious problem, and you should never ignore it. If you have COPD and experience significant unexplained weight loss, you should schedule an appointment with your doctor without delay.
How to Gain Weight and Build Muscle Mass with COPD
Since weight loss and muscle wasting is such a common and serious problem for people with COPD, researchers have spent a lot of time studying how to prevent it. Luckily, scientists have so far found a variety of methods to reduce muscle wasting and help COPD patients build muscle mass more effectively.
The Importance of Strength Training

Many people with COPD have difficulty exercising, and for a long time researchers believed that breathing difficulties were the main cause. However, it turns out that lack of muscle strength, not just shortness of breath, is the culprit behind many COPD patients' lacking tolerance for exercise.
Because of this, researchers believe that strength training is one of the most important things you can do to improve your health when you have COPD. It not only prevents muscle wasting, but also can improve your exercise endurance, emotional health, and overall quality of life.

In fact, studies comparing COPD patients who followed an exercise plan focused on aerobic activity with patients who followed a strength training regimen show that strength training often leads to better outcomes. Patients who undergo strength training tend to see the biggest improvements in their muscle mass and exercise tolerance.
What is perhaps most telling, however, is the fact that COPD patients who do strength exercises report the largest improvements to their quality of life. This is likely because strength training helps patients feel stronger, gain mobility, and do more daily activities without feeling tired and fatigued.
Strength training is like a positive feedback loop that leads to better strength, better mood, and better health. It goes like this:
-
The more muscle you build, the more exercise you will be able to handle. The more exercise you can handle, the more muscle you can build.
-
The more muscle you build, the better you can manage your COPD symptoms. The better you can manage your COPD symptoms, the more you can exercise.
-
The more you exercise, the less depressed and anxious you will feel. When you feel less depressed and anxious, it makes it easier to exercise and eat a healthy diet.
-
When you eat a healthy diet, your body is better nourished. When you're better nourished, you'll have more energy, which allows you to build even more strength.
- The stronger you are and the better you can manage your symptoms, the more mobile and active you can be in your daily life. This leads to even more physical activity, more strength, and a better quality of life overall.
Strength Training Exercises for COPD

Resistance exercises like push-ups, squats, and weight lifting are the most effective ways to build body strength and muscle mass. Many people enjoy strength training using weights and other equipment you can find at the gym, but you can also do effective strength training exercises with minimal equipment at home.
You can buy a small set of light free weights for lifting at home and choose exercises that use your own body weight as resistance to build strength. If you have severe COPD symptoms or limited energy, there are a variety of chair exercises you can do that are designed specifically for people with limited strength and mobility.
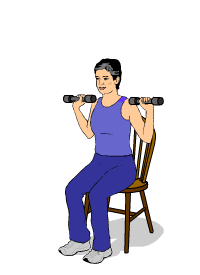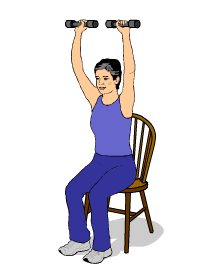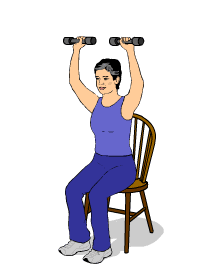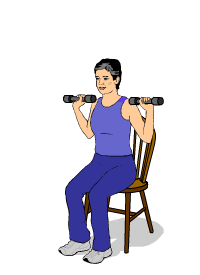
Most doctors recommend doing strength training sessions at least three days a week in order to see an improvement in strength and muscle mass. You should start slow, doing only as much as you can handle without feeling too breathless or fatigued.
You can add in extra muscle groups and repetitions as time goes on and your strength and endurance increases. Just make sure you talk to your doctor before starting any new exercise routine, and don't be afraid to ask for advice, either.
Here are some examples of resistance exercises you can do to build strength and muscle mass:
- Leg lifts
- Bicep curls
- Squats
- Knee raises
- Chair exercises
If you are having difficulty exercising on your own, consider joining a pulmonary rehabilitation class. It's like a special exercise and education course for people with respiratory diseases, and doctors recommend it to anyone who has COPD and struggles to keep up with their exercise plan.
At pulmonary rehabilitation you can learn how to better control your symptoms when you exercise, use your medications effectively, and even get opportunities to learn and practice new exercises. They often also include dietary education, mental health support, and group therapy sessions to allow patients to share their worries, struggles, and successes.
Use Supplemental Oxygen

Shortness of breath is one of the major barriers that prevents many people with COPD from exercising and eating as much as they should. Luckily, many patients find it much easier to do both of these things when they use supplemental oxygen at the same time.
Using supplemental oxygen at mealtimes can reduce breathlessness and fatigue while you eat, making it easier to get the calories and nutrients you need to stay healthy. When you exercise, supplemental oxygen can help you keep your respiratory symptoms under control so you can have better endurance and build more muscle.
If you regularly struggle to breathe when you exercise or when you eat, talk to your doctor about using supplemental oxygen during these activities. Your doctor will assess your lung function to determine your oxygen needs and help you learn how to manage your oxygen flow and concentration when you do different activities.
Talk to Your Doctor about Supplements
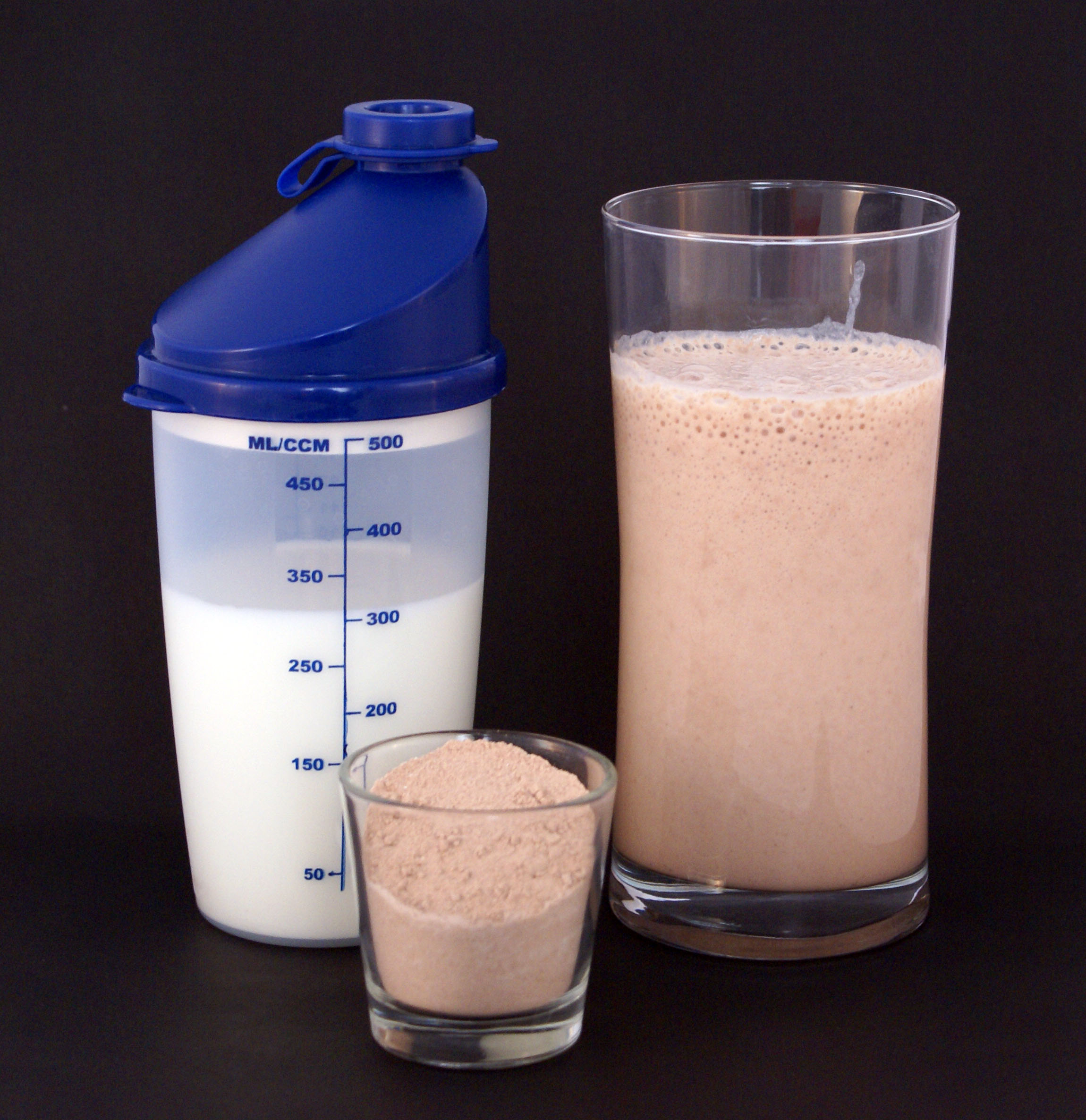

When it comes to building muscle and maintaining a healthy weight, many COPD patients need some extra help. Studies show that supplementing your diet with certain nutrients like protein or creatine can prevent muscle wasting in people with COPD and help them gain weight and muscle mass more quickly.
Some doctors recommend protein shakes or other nutrient-rich shakes to people with COPD who have trouble getting enough calories from their meals. Shakes are quick and convenient to prepare, and take very little energy to drink compared to solid foods.
It is important to always get your doctor's approval before taking new supplements, using nutrient shakes, or significantly changing your diet in any way. Your doctor can ensure that what you're taking is healthy and won't interfere with any of your other treatments or medications.
Supplements known to improve muscle and weight gain in patients with COPD:
- Creatine
- Protein shakes
- High-calorie nutrient shakes
Eat More Meals

When you eat a lot of food all at once, it can cause your stomach to expand and press on your lungs. For people with COPD (and especially emphysema), this is a common problem that can cause extreme discomfort and make it difficult to breathe during and after meals.
These symptoms can make it difficult to finish meals or cause people with COPD to dread or avoid eating food. That's why doctors recommend patients who struggle with breathlessness at mealtime to change their eating schedule to include more meals and smaller portions.
Instead of three large meals a day (breakfast, lunch, and dinner), many doctors recommend that people with COPD eat six smaller meals spaced out throughout the day. Doing this cuts the size of each meal in half and gives your stomach time to digest and empty in-between meals.
This way, you can eat smaller portions that won't cause discomfort but still get enough food to prevent weight and muscle loss. It's a great solution if you struggle with breathlessness because it allows you to get all the calories and nutrients you need with a much lower risk of triggering breathing difficulties at mealtimes.
Prioritize Your Food

If you have trouble finishing meals because of breathlessness or other COPD symptoms, it can be helpful to prioritize the food on your plate. Eat the most calorie-dense and nutrient-dense foods first, that way you get the most out of your meal even if you can't finish it all.
If you often feel full or breathless before finishing a meal, it can also help to limit the amount of water and other liquids you drink. If you avoid drinking before or during meals, you'll have more room in your stomach for food. You can make up the fluids by drinking more water in-between meals, instead.
If you have trouble building up an appetite, try starting your meals with a treat or a food that you really enjoy. You will dread eating less if you have something to look forward to, and starting with a favorite food might whet your appetite and make it easier to continue eating.
Here are some examples of nutrient-dense foods to add to the beginning of your meals:
- Eggs (cooked in oil)
- Nuts and nut butters (e.g. peanut butter)
- Milk and cottage cheese
- Meats (chicken, fish)
Eat More Protein

Protein is necessary for your body's basic functions, and it's something your body absolutely cannot do without. If you don't get enough protein in your diet, your body will take it from the next-best source: your muscles.
This type of muscle wasting is a problem that happens often in COPD patients who are weak and malnourished. That's why it's so important to maintain a healthy diet when you have COPD.
When the food you eat isn't enough to meet your body's energy and nutrient requirements, your body will not hesitate cannibalize your own muscles for the nutrients it needs. The solution is to make sure that you are eating enough and have a balanced diet with protein-rich foods.
Most doctors recommend that you get most of your protein from lean meats and plant protein sources. Adding extra portions of chicken, fish, eggs and beans to your meals is a healthy way to add more lean protein into your diet.
On the other hand, you should avoid the less-healthy fatty meats and processed meats like bacon, sausage, and ham. Also, if you need to make room for more protein in your diet, it's best to eat fewer simple carbs like sugars, white breads, and white pastas.
Here are some examples of healthy proteins to add to your diet:
- Fish (salmon, cod, tuna, etc.)
- Chicken
- Lean beef
- Eggs
- Tofu
- Beans & Legumes
Consult a Dietitian
Sometimes, no matter how hard you try, you just can't manage a healthy diet on your own. COPD can make getting proper nutrition very difficult, especially because it causes you to need extra calories and nutrients.
If you have trouble gaining muscle or continue to lose weight despite your best efforts, it's time to talk to your doctor or a licensed dietitian. They can help you figure out exactly how many calories you need to eat and what amounts of different nutrients your bo

If you have COPD, then you know that all kinds of unexpected things can affect your symptoms and make them worse. Even minor respiratory irritants, like fragrances, air pollution, and dry air, can make it more difficult to breathe.
That's why, when the seasons shift, it's important to understand how the change might affect your COPD. This is particularly true when moving from the mild fall season into harsh winter conditions.
As the cold weather sets in, you should be aware of all the potential COPD hazards that winter weather brings. Then, you will be better prepared to manage your symptoms and deal with the challenges when they come.
In this guide, we're going to walk you through all of the most common challenges COPD patients face during the winter time. We'll warn you about winter respiratory irritants, weather hazards, and other seasonal conditions that could make your symptoms worse.
We'll also show you what you can do to prepare for these problems and minimize their impact on your lungs. That way, instead of spending the winter months struggling to manage your disease, you can use the tips and tricks in this guide to overcome winter challenges and breathe much better this season.
Things You Should Know and Prepare for This Winter if You Have COPD
Extra Difficulty Breathing Winter Air
You might have noticed on your own that breathing cold, winter air can make it more difficult to breathe. This can happen to healthy adults but it is particularly problematic for people with COPD.
That's because winter air is usually far from the optimum temperature and humidity that your lungs and airways prefer. Cold, dry air is much harsher to breathe than warmer, humid air, and it can irritate your lungs and constrict your airways as you breathe.
When the humidity is very low, the dry air sucks the moisture out of your airways. This thickens your mucus and irritates the tissue that lines your nose and airways, triggering symptoms like coughing and shortness of breath.

The cold temperature of the air alone can also be a problem, especially when you first go outside after breathing warm indoor air. When you take a breath and suddenly bring frigid air into your lungs, it can trigger bronchospasms, which constrict your airways and make it harder to breathe.
The best way to avoid these problems is to avoid breathing the cold, dry winter air as much as you can. That means staying indoors when weather conditions are bad and using simple techniques to warm up the air that you breathe.
This is easier to do if you check your local weather forecast regularly and plan ahead for upcoming conditions. Pay special attention to the temperature and humidity, and be prepared to take extra measures to manage your symptoms on particularly harsh days.

When you do have to go out in the cold, you can make the air more breathable by covering your nose and mouth with a scarf or a special cold-weather mask (called a CT mask). This will trap heat and moisture from your breath, helping to warm and humidify the harsh outside air so it is more comfortable to breathe.
Here are some tips to help you breathe better in the frigid winter air:
- Avoid going outside during the coldest parts of the day.
- Stay indoors during inclement weather and when the temperature is very cold.
- Don't try to exercise outdoors when the air is too cold or dry.
- Wrap a scarf or cloth around your mouth to breathe easier in cold air (or wear a CT mask). https://lunginstitute.com/blog/ct-masks-for-copd/
- If you use oxygen therapy, use a humidifier bottle to moisturize the air that comes from your oxygen source.
- Practice pursed-lips breathing when you feel short of breath in cold weather.
- Continue taking your maintenance medications exactly as your doctor advises.
- Always bring your rescue inhaler with you whenever you leave your home during the winter, especially during harsh weather.
Danger During Cold and Flu Season
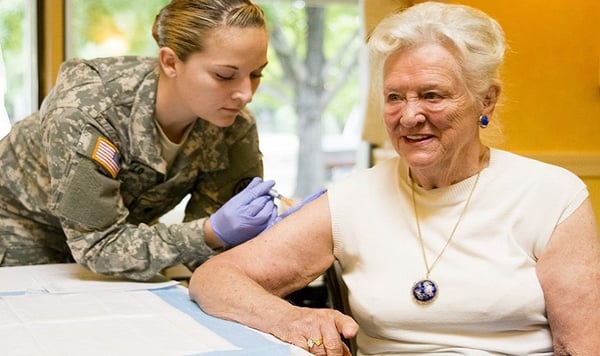
Along with winter comes cold and flu season, that dreaded time of year when contagious respiratory illnesses reach an all time high. This time of year poses a special danger to people with COPD, who are more prone to getting sick.
While a common cold might not seem like a big threat, a minor illness like a cold can turn into something much more serious if you have COPD. Any kind of respiratory illness can trigger severe COPD symptoms and lead to more serious exacerbations.
COPD exacerbations are difficult to treat and, in the worst cases, can cause life-threatening complications. Even minor COPD exacerbations can make you feel very sick and take a major toll on your life, disrupting your ability to exercise, work, and do other normal activities.
COPD exacerbations can also take a very long time to recover from, and in some cases can result in permanent lung damage that makes your symptoms permanently worse. That's why it is so important to practice good hygiene, keep your immune system healthy, and avoid contagious illnesses if you have COPD.
Unfortunately, studies show that people with COPD are more than twice as likely to experience an exacerbation during the winter months. That means you need to take extra special precautions during this season to avoid getting sick.
That means doing what you can to bolster your immune system and keeping your COPD symptoms under control. It also means coming up with strategies to help you avoid germs and germ-heavy environments, especially during peak cold and flu season.

The best way to do this is to keep up-to-date with your vaccinations and be diligent about your personal hygiene. Especially when you're out in public, be cautious about what you touch and avoid transferring germs from your hands to your eyes, nose, and mouth.
Wash your hands often, avoid people who are sick, and be especially cautious in crowded places. If you use oxygen therapy, you should be extra diligent about keeping your medical equipment (like your nasal cannula) clean during the winter.
Here are some additional tips to help you prepare for cold and flu season:
- Get your yearly influenza vaccination.
- Ask your doctor if you need a pneumococcal (pneumonia) vaccine.
- Take all of your medications as directed by your doctor and take care not to miss a dose.
- Know the early signs of a COPD exacerbation and what you should do when you notice your symptoms starting to get worse (follow your COPD action plan).
- Practice proper personal hygiene at home and especially in public.
- Wash your hands often and avoid touching your face, especially in public places.
- Avoid attending crowded events during cold and flu season.
- Do your best to stay away from anyone who has a contagious illness, including avoiding houses or events where someone there is sick.
- Quit smoking to reduce your risk of respiratory illnesses and infections.
Extra Fatigue and Worse Symptoms in Cold Weather
.png?width=155&name=thermometer-151236_1280(1).png)
Even if you protect your lungs from pollution and dry air this winter, the bitter cold can still bring you down. Cold temperatures alone can have a noticeable effect on COPD symptoms, and this effect can even last for several days.
Studies show that breathing cold air can hurt your lungs and reduce their ability to function by a measurable amount. It causes your airways to constrict and can even damage the tissue lining your airways, making it more difficult to breathe.
However, even just being in the cold air—not even breathing it—can reduce lung function and worsen COPD symptoms. Even short periods of exposure to cold weather can trigger breathlessness, fatigue, and a significant increase in the number of COPD patient hospitalizations.
These effects are likely caused, at least in part, by how your body reacts to getting cold. In an effort keep your core temperature from falling, your body has to work harder and burn extra energy to stay warm.
When you're exposed to very cold temperatures, this can drain your energy levels and cause you to feel fatigued. It also requires your lungs to work harder to keep pace, which puts extra strain on your respiratory symptom and makes it more difficult to breathe.
Many studies have linked worsened COPD symptoms with cold outdoor temperatures and even cold temperatures indoors. Some studies show that cold temperatures can double COPD patients' risk for exacerbations and even increase their risk of death.
That's why you should be prepared to experience worsened COPD symptoms when the temperature drops this winter. That means keeping your rescue inhaler handy and making sure you have a warm place to go when extremely cold weather hits.
During the coldest months of the year, keep a diligent eye on your local weather forecast so a cold snap doesn't take you by surprise. When you're expecting extra chilly weather, make preparations to stay warm and avoid spending time outdoors.
When you do go out, don't take any chances and always dress appropriately warm. Even if it adds a few minutes to your usual routine, bundling up is your best defense against the harsh winter temperatures that could worsen your COPD.
Most importantly, make sure you have a reliable heating system that can keep your home at a comfortable temperature all winter. You should also make sure you have somewhere to go if your heater breaks down or your house loses power during a storm.
Here are some tips for combating cold temperatures this winter:
- Avoid exposing yourself to cold weather and spend as little time outside as possible on especially frigid days.
- Always check the weather before you leave the house and wear appropriately warm and comfortable clothes.
- Wear layers so you can stay warm in the cold but also stay comfortable indoors by removing unnecessary layers.
- When you do go out in the cold, cover as much skin as possible; don't skimp on cold weather gear like hats, scarves, mittens, leg warmers, and earmuffs.
- Avoid clothes that are too tight—especially around the chest—because they can restrict your movement and breathing.
- Make sure to keep your house at a warm, comfortable temperature at all times during the winter.
- Consider changing your plans so that you can stay indoors during particularly cold or harsh weather. (e.g. work from home or reschedule other outings and errands)
- Make a special effort to avoid going out in cold weather when you are not feeling well or are experiencing a COPD exacerbation.
- Be prepared to use your rescue inhaler more often and bring it with you anytime you leave your home.
- Keep extra food and supplies at home just in case cold or inclement weather keeps you home-bound for an extended period of time.
- Ask a friend or family member to check up on you during cold spells and winter storms
Fewer Exercise Opportunities

If you have COPD, you shouldn't exercise outdoors when the weather is bad or the air is cold and dry. This means you will need to do the majority of your physical activity indoors during the winter months.
Exercise is one of the best ways to keep your heart and lungs healthy, which is why it's vital to keep it up all throughout the year. Even though you might be tempted to hide away and hibernate this winter, you shouldn't let the cold weather get in the way of your exercise goals.
Without outdoor sports and activities to keep you active, you might need to be more creative and deliberate with your workouts. Be prepared to rework your exercise routine and find new ways to get physical activity indoors.

For example, if you are used to walking outdoors for exercise, you could walk on a treadmill or indoor track at the gym instead. You could also take walks in a large public building in your area, such as an indoor mall.
You might also consider joining an exercise class at a local gym or fitness center. Many people find that participating in this kind of scheduled group activity makes it easier to stay motivated and stick with an exercise routine.
If you'd like, you can even work out in your own home without needing any expensive equipment. All you have to do is find a home exercise routine you like, whether it's online, on DVD, or a routine you devise yourself.
Don't ever think that staying inside means that you can't also stay active. Winter exercise opportunities are essentially endless, even though they might be tricky to find.
Here are some tips to help you get more exercise this winter:
- Join a gym where you can walk and do other exercises indoors.
- Clear some floor space in your house to practice simple indoor exercises at home.

Even if you are not short of breath, or experiencing symptoms of breathlessness, you blood oxygen levels could be dangerously low! Read this blog to learn about how much oxygen you are getting compared to how much you need.
The hallmark symptoms of COPD are shortness of breath, or feeling breathless. It's certainly one of the most common symptoms, as well as that most invasive. Whether you're the person with COPD or the caregiver, shortness of breath is scary and unsettling for everyone involved.
There are devices called pulse oximeters, which measure your oxygen saturation levels. This is important for COPD patients to know how much oxygen they are able to process. Pulse oximeters have become more popular and accessible in recent years.
{{cta('fa8abc2a-1e88-4fa3-82fd-1cb5b9ed43b2','justifycenter')}}
This is both a good and bad thing because COPD patients may be relying as much on their oximetry results as their actual symptoms when evaluating their breathing capabilities. It can cause a lot of confusion.
The confusion comes from having a "normal" oxygen saturation level, but still feeling extremely short of breath. Also, it might be hard to notice any symptoms even when your oxygen saturation levels are dangerously low.

We are going to clear up this confusion in this blog.
The Difference Between Shortness of Breath and Being Hypoxic
There are the three main factors that impact how well your body is able to take up and use oxygen.
- How well your lungs absorb oxygen into your body and release carbon dioxide.
- How well your heart is able to pump oxygen throughout your body.
- How well your cells and muscles use the oxygen they get from your blood.
Obviously, various diseases like COPD or heart disease will inhibit some or all three of those factors. COPD causes intense lung damage, and even cardiac problems, that definitely can impact all three of these.Treatment methods including medication, supplemental oxygen therapy, and exercise can help in improving the way your body utilizes oxygen, and in turn, making you less short of breath.
Feeling breathless
Have you ever felt yourself gasping for air, or feeling out of breath even when you’re not exerting yourself? Well this can happen to anyone, and while it is a common symptom of COPD, not everyone who feels short of breath has COPD.
![]()
Breathlessness is associated with lung damage and/or airway inflammation but it can also be caused by:
- Heart health
- How fit you are
- Emotions
- Weather
- Altitude
- Infection
- Low red blood cell count (anemia)
![]()
Even if you are t feeling breathless, this does not always mean that you are hypoxic.
Being Hypoxic or Having Hypoxemia

There is a difference between hypoxemia and being hypoxic. Hypoxia is when there is a low level of oxygen in your blood. Being hypoxic means that not enough oxygen is getting to your body's cells.
These impact your body at two different stages when your body is working to absorb oxygen.
You can find your oxygen saturation level and test whether or not you have these conditions. There are two ways to measure it:
- Arterial blood gases test. This takes place at your doctor’s or a with a lab tech
- Using a pulse oximeter. This you can do on your own, and the small device fits over a finger tip. It uses infrared rays to measure the percentage of oxygen in your blood.
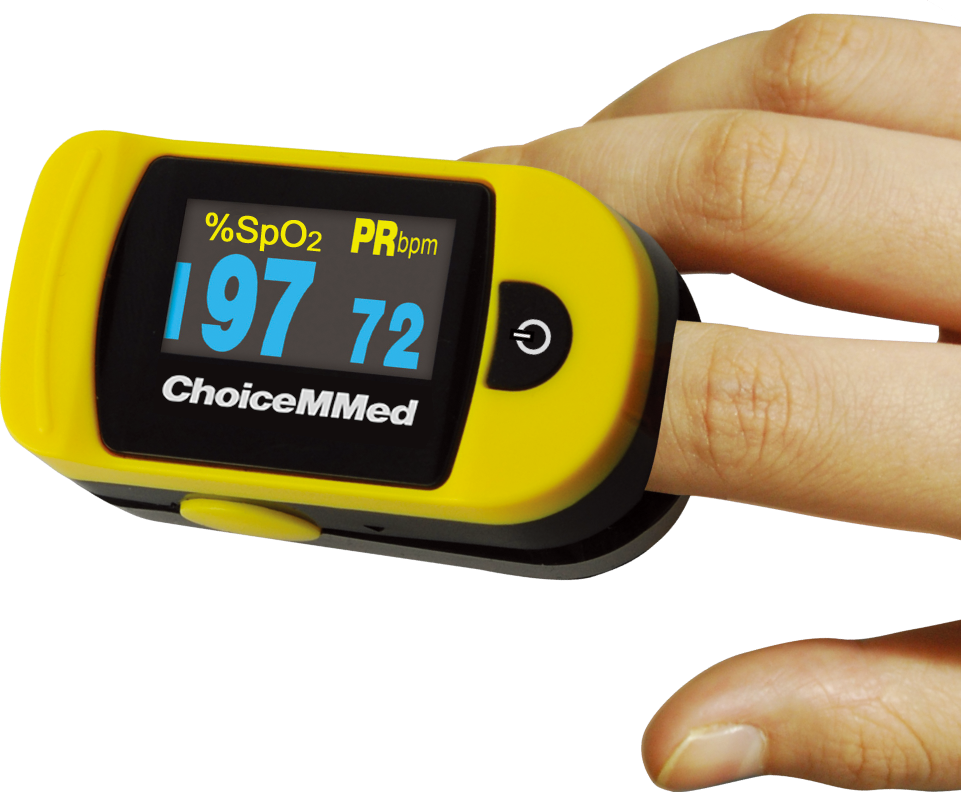
Oxygen saturation is largely dependent on your overall health. This can be indicated by how fast you are breathing during activity and rest.
A typical healthy person has oxygen saturation levels that range from 95 to 100%.When saturation levels drop to 90% and below that is considered low and unhealthy. COPD patients often dip below 90% at times.
Feeling Breathless But Not Hypoxic
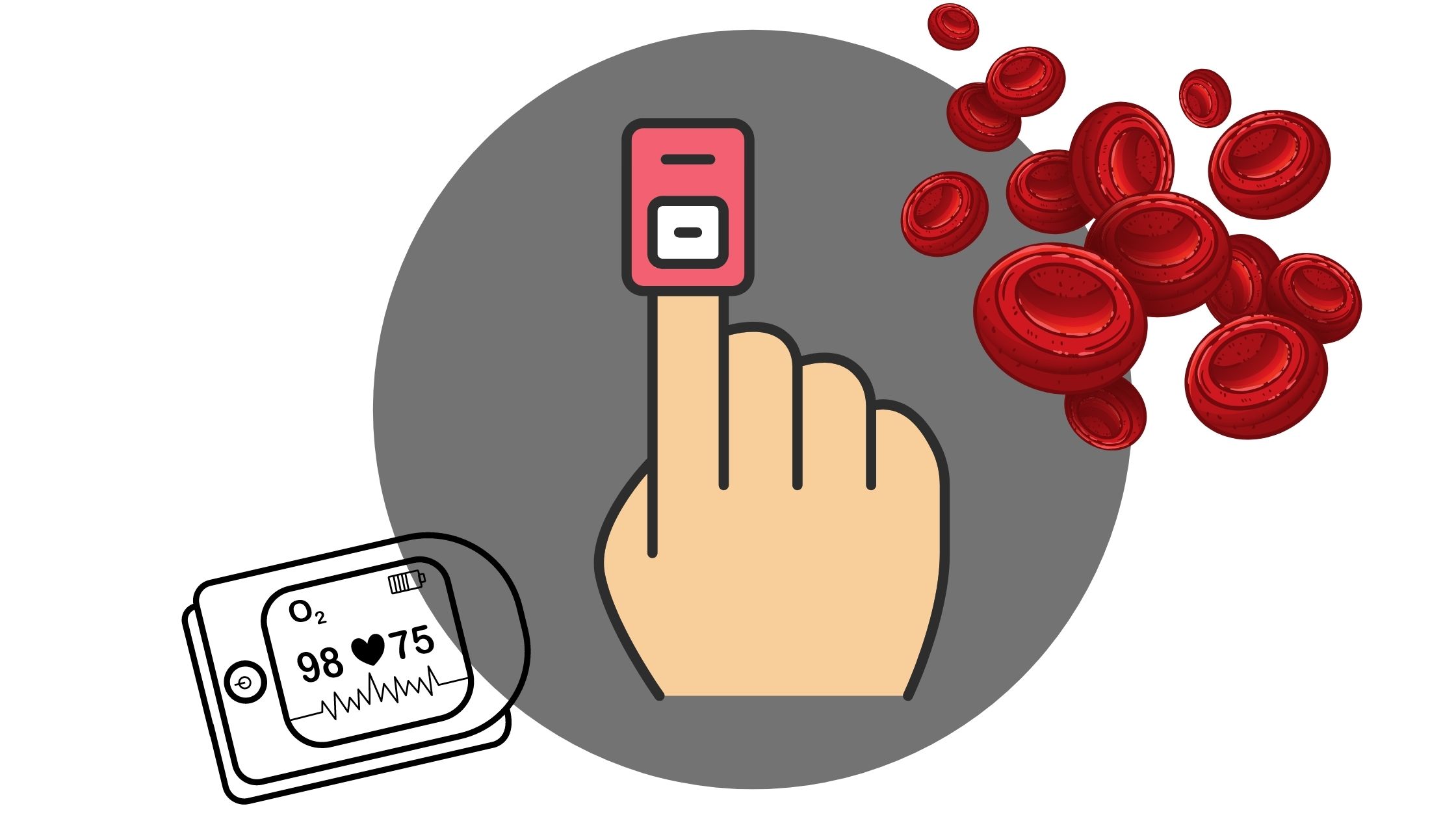
Now that you have an understanding of oxygen saturation, and the symptoms associated with low levels of oxygen, you might be wondering, “Why am I so short of breath, but my oxygen levels are still normal?"
Well, even if you're experiencing extreme breathlessness, but your oxygen saturation levels remain in that 95% - 100% healthy range, then supplemental oxygen will not solve your problem.
Instead, you need to learn how to recover from breathlessness. Try stopping what you’re doing and resting right away.

After stopping the action that caused your breathlessness try these additional actions:
- Remind yourself that you know what to do. Taking action can help you overcome the anxiety that often goes along with being short of breath.
- Position yourself to breathe easier. Leaning forward or bending over helps drop your abdomen away from your lungs, making breathing easier. Lean your arms on your knees or on some stationary object like the wall or a counter. (I remember often seeing my dad doing this, especially after a severe coughing spell.)
- Work on controlling your breathing. If you know how to do diaphragmatic or pursed lip breathing, then do so. If you haven't learned those techniques yet, then at least work on slowing and deepening your breaths in and out.
- Once you are feeling better and more in control of your breaths, it may be time to resume whatever you had been doing. But you may need to modify the intensity to avoid re-triggering your breathlessness.
Pulmonary rehab is another great tool that can be beneficial in teaching you how to avoid and/or deal with this symptom. These are classes you take with trained professionals, they teach you breathing exercises and physical activities that are good for your level of health.
You can also look into a rescue, or quick-relief, inhaler. Talk with your doctor about these options, because they can offer some relief in your situation.
Hypoxic But Not Feeling Breathless

Even if you are not feeling at all breathless, your oxygen levels can still be low, and this is an important concept to understand. Low oxygen saturation levels are not healthy, do not ignore it. Get your oxygen levels tested regularly, even if you are not short of breath.
If you do measure low oxygen levels during a blood test, or while conducting pulse oximeter tests. Speak with your doctor right away about the next steps you must take to get your levels to normal.
This is often when people need a portable oxygen concentrator to use as their additional source of oxygen. Devices like the Inogen One G5, and the ARYA P5 Portable Oxygen Concentrator often oxygen patients medical grade oxygen they can use 24/7.
It means your blood and tissues are not getting the oxygen they need to survive, and it needs to be addressed right away.
The answer to hypoxia is supplemental oxygen therapy. However, how much and how often you need oxygen depends on the progression of hypoxia you are experiencing and your health care team will determine this. It is also important that your healthcare team helps you with a plan for how often to measure your oxygen levels with a home pulse oximeter.
Overview

If you have COPD, remember that shortness of breath (and other symptoms, such as coughing) are an important thing to take note of. Track your symptoms to measure your current health status and how your health changes over time.
As far as knowing your oxygen saturation level, you will need to monitor this regularly because even if you are not short of breath your oxygen levels could be low, and that is dangerous. This is around the time you will need to call LPT Medical at 1+(800)-946-1201 to talk about your oxygen device options. On the other hand, and unfortunately so, it is entirely possible to be short of breath, but have healthy oxygen saturation.


 So we can find the best portable oxygen concentrator for your needs!
So we can find the best portable oxygen concentrator for your needs!















